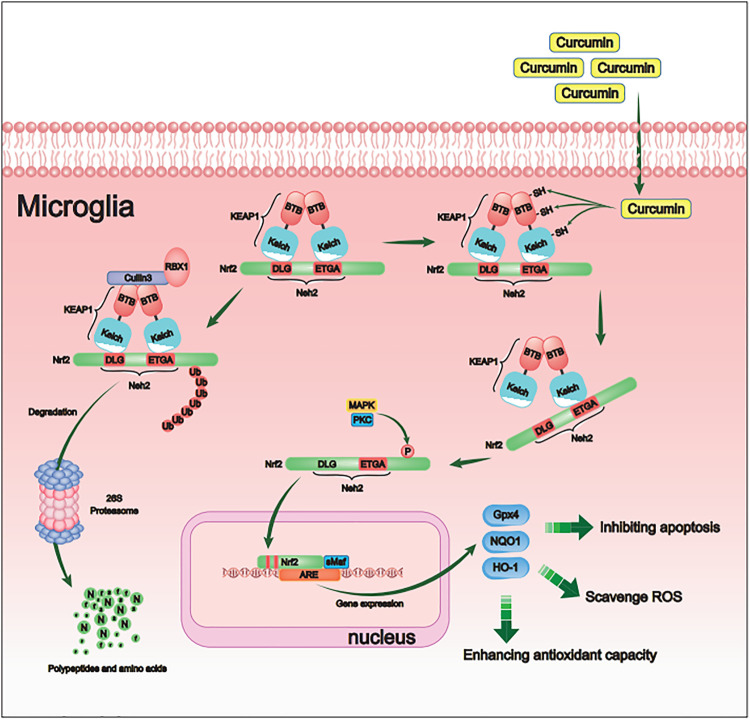
FIGURE 9.
Schematic diagram of the molecular mechanism by which curcumin promotes antioxidant activity of intracranial microglia after intracerebral hemorrhage. By activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway, curcumin promoted the expression of many downstream antioxidant-related genes (including HO-1, NQO1, and Gpx4). Therefore, curcumin inhibited the cerebral oxidative injury after ICH.