Figure 1. Synthesis and characterization of “pseudovirus-like” nanoparticles.
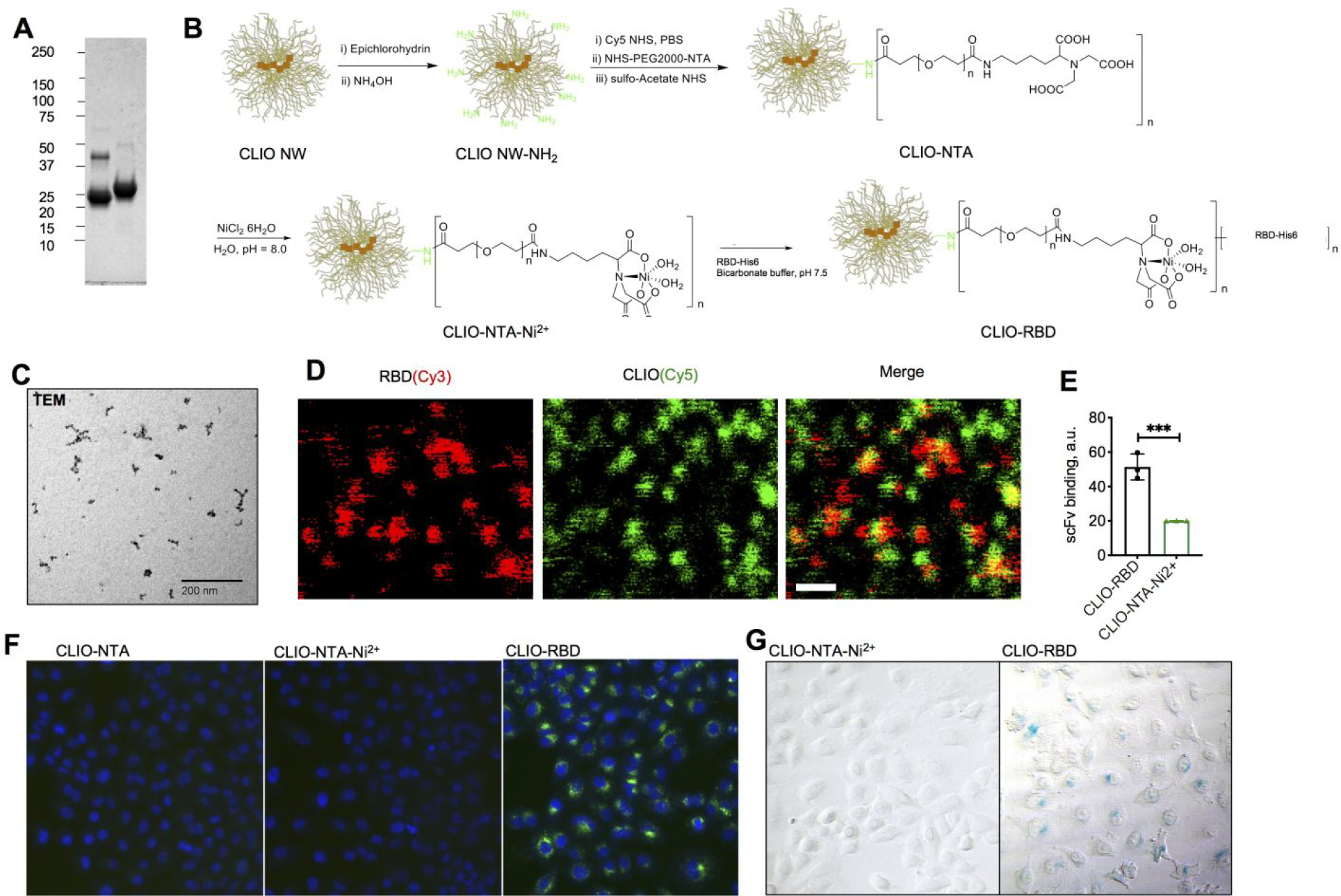
A) Purified His-tagged RBD (from left to right: non-reduced and reduced forms); B) synthesis of CLIO-RBD starting from crosslinked dextran iron oxide nanoworms (CLIO NW); C) transmission electron microscopy of CLIO-RBD shows electron-dense iron oxide cores (the shell and the ligand are not visible); D) high magnification confocal microscopy of CLIO(Cy5)-RBD(Cy3). Size bar, 0.5μm. Nanoparticles appear larger than the optical resolution limit due to the fluorescence halo; E) binding of anti-RBD single chain antibody to nanoparticles in full serum (prepandemic). ***p<0.001; F) uptake of control and RBD-modified particles (Cy5 labeled) by human ACE2-expressing A549 cells by fluorescence microscopy and G) Prussian blue staining. Incubation conditions are in Methods. The experiment was repeated twice.
