FIGURE 3.
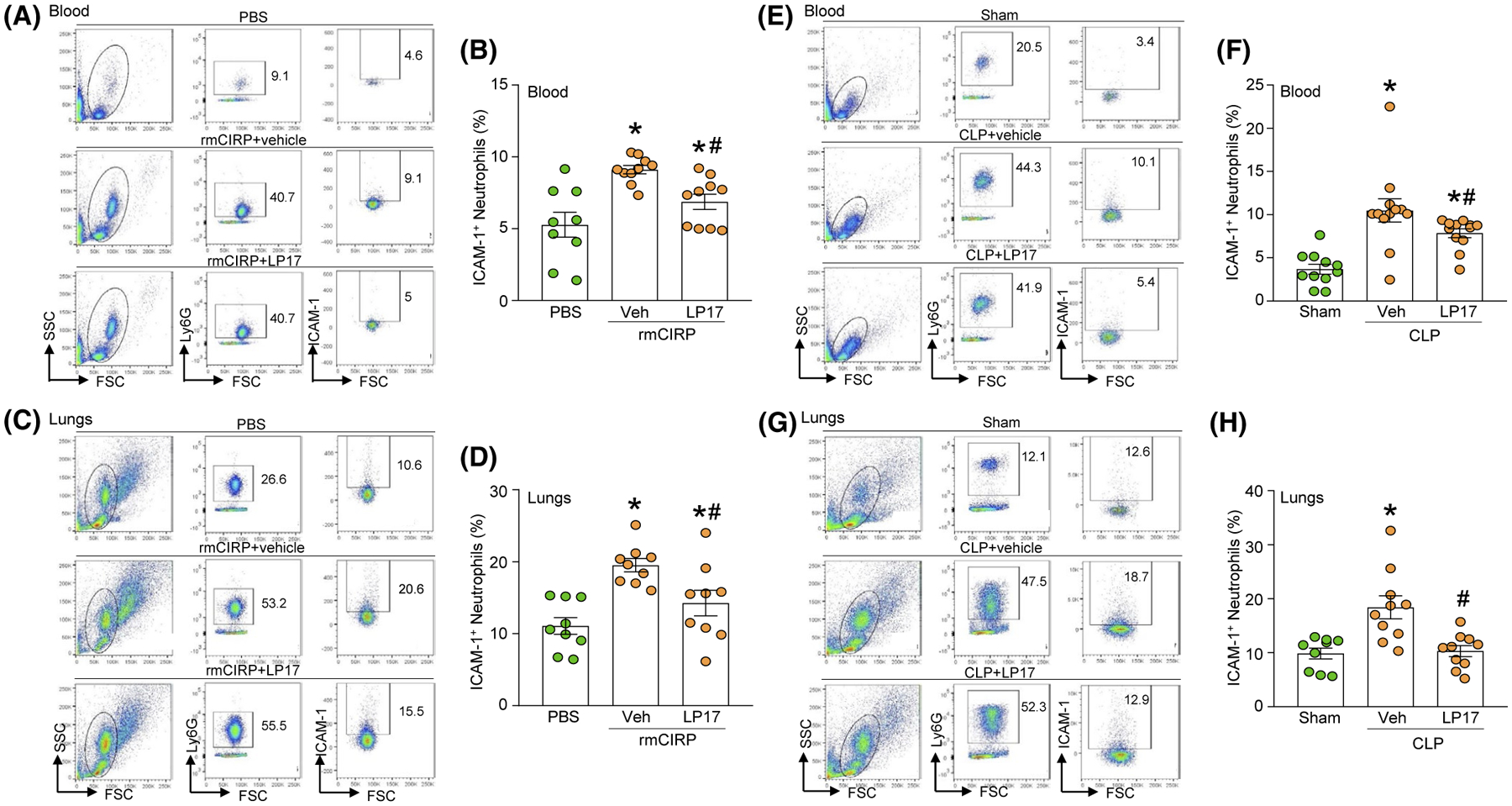
LP17 inhibits ICAM-1 expression in blood and lung neutrophils in rmCIRP-treated or septic mice. Mice were injected with PBS or rmCIRP (5 mg/kg BW) intraperitoneally (i.p.). At the same time mice were i.p. injected with vehicle (PBS) or LP17 (5 mg/kg BW). After 4 hours of injecting PBS, rmCIRP, vehicle, and LP17 mice were sacrificed to collect (A, B) blood and (C, D) lungs to determine ICAM-1 expression in neutrophils. Single cell suspension of blood and lungs were stained with APC-Ly6G and FITC-ICAM-1 Abs. ICAM-1 expression in LY6G+ cells were determined by flow cytometry. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 9 mice/group). The groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and SNK method (*P < .05 vs PBS-treated mice (without rmCIRP treatment); #P < .05 vs vehicle + rmCIRP-treated mice). E-H, Sepsis was induced by CLP in WT mice. Mice were instilled with vehicle (PBS) or LP17 (5 mg/kg BW) in 100 μL volume in the peritoneal cavity at the time of CLP operation before closing the abdomen. Mice undergoing only laparotomy without cecal ligation or puncture served as sham group. Four hours after sham or CLP operation, mice were sacrificed to collect blood and lungs. Single cell suspensions of (E, F) blood and (G, H) lungs were stained with APC-Ly6G and FITC-ICAM-1 Abs. ICAM-1 expression in LY6G+ cells were determined by flow cytometry. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 11 mice/group). The groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and SNK method (*P < .05 vs sham mice; #P < .05 vs vehicle-treated CLP mice)
