FIGURE 4.
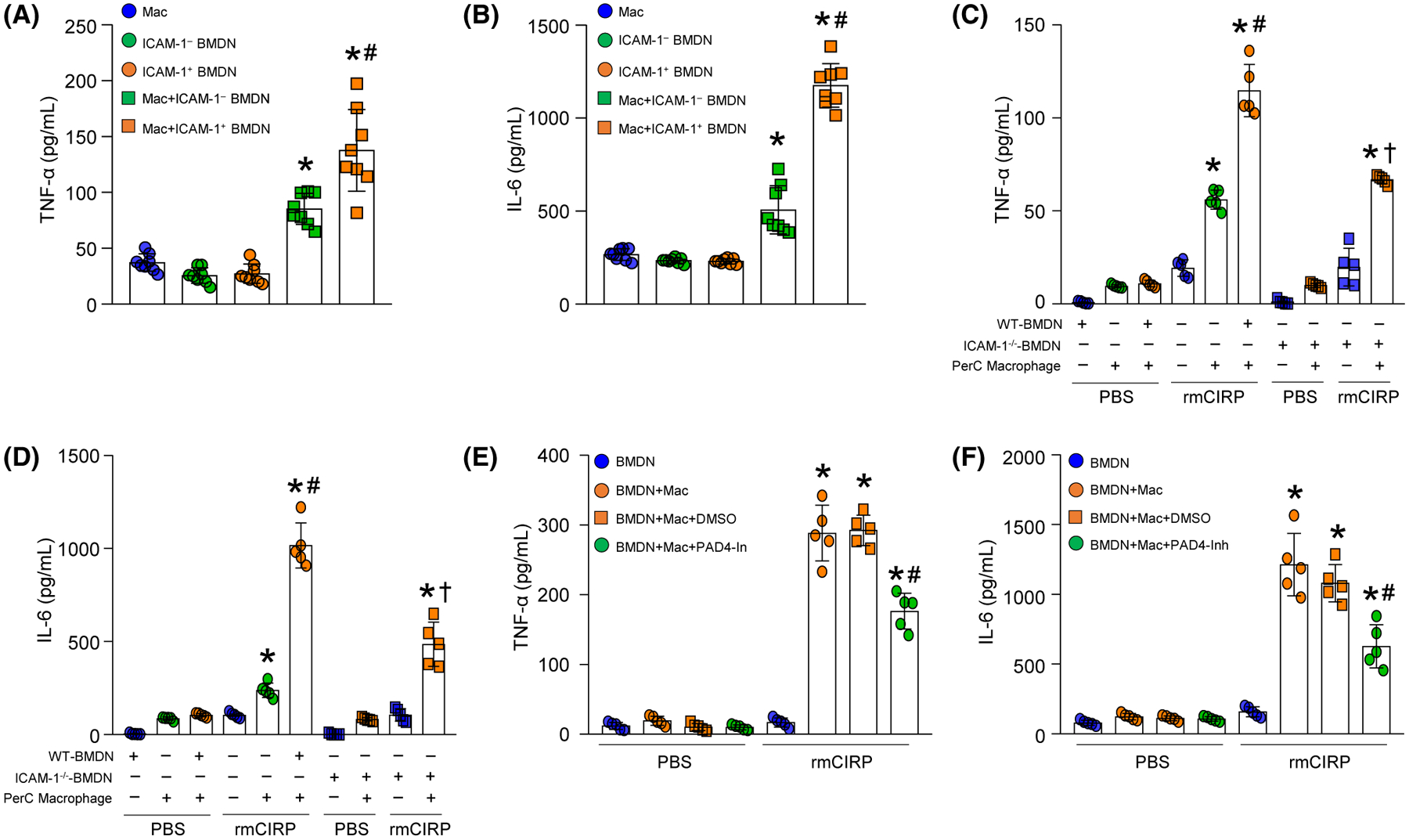
ICAM-1+ neutrophils induce macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines through increased NET formation. A total of 5 × 104 ICAM-1+ or ICAM-1− neutrophils sorted from rmCIRP-treated BMDN were cocultured with 1.5 × 105 peritoneal (PerC) macrophages, and 20 hours of coculture (A) TNF-α and (B) IL-6 levels in the culture supernatants were assessed by ELISA. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 8 samples/group). The groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and SNK method (*P < .05 vs macrophage only; #P < .05 vs macrophage + ICAM-1− PMN). C, D, BMDN (5 × 104) isolated from WT and ICAM-1−/− mice were cultured separately with PerC macrophages (1.5 × 105). After 20 hours of stimulation with rmCIRP (1 μg/mL) (C) TNF-α and (D) IL-6 levels in the culture supernatants were assessed by ELISA. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5 samples/group). The groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and SNK method (*P < .05 vs PBS macrophages; #P < .05 vs rmCIRP macrophages; †P < .05 vs rmCIRP macrophage + WT-PMN). E, F, WT BMDN (5 × 104) cocultured with PerC macrophages (1.5 × 105) were simultaneously treated with PAD4 inhibitor CI-amidine at a dose of 5 μM and rmCIRP (1 μg/mL). After 20 hours of stimulation with rmCIRP, (E) TNF-α and (F) IL-6 levels in the culture supernatants were assessed by ELISA. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5 samples/group). The groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and SNK method (*P < .05 vs PBS macrophages; #P < .05 vs rmCIRP macrophages + DMSO)
