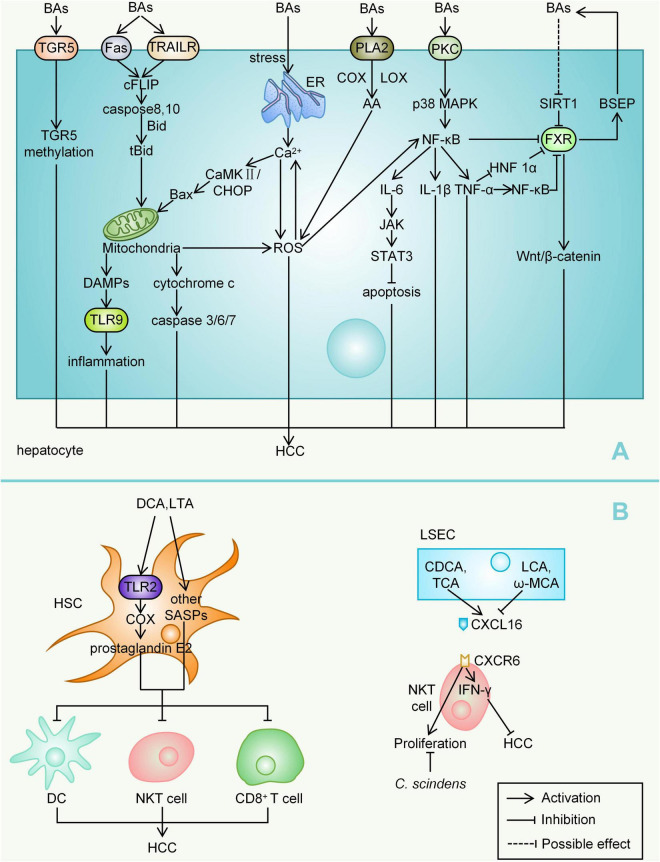
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms by which BAs mediate HCC. (A) Bile acids, as important metabolites of the gut microbiota, can cause inflammatory responses, cell death, ROS accumulation, reduction of apoptosis, and so on, mainly by mediating complex signalling pathways within hepatocytes, ultimately leading to the development of HCC. (B) BAs can also act on other liver cells such as HSC, LSEC, NKT cell, and so on, thereby affecting HCC progression. BAs, bile acids; TRAILR, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor; cFLIP, Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; Bcl-2, B cell lymphoma-2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR, Toll-like receptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; PKC, protein kinase C; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PLA2, phospholipase A2; AA, arachidonic acid; COX, cyclooxygenase; LOX, lipoxygenase; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; Egr-1, early growth response gene 1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; vcm-1, vascular endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; FXR, Farnesoid X receptor; TDCA, taurodeoxycholic acid; TCA, taurocholic acid; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; FasL, fas ligand; HNF 1α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α; TGR5, Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; LTA, lipoteichoic acid; SASP, senescence-associated secretory phenotype; DCs, dendritic cells; NKT cell, natural killer T cell; CXCR, C-X-C chemokine receptor type; LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; LCA, lithocholic acid; ω-MCA, ω-muricholic acid; NK cell, natural killer cell.