Fig. 3.
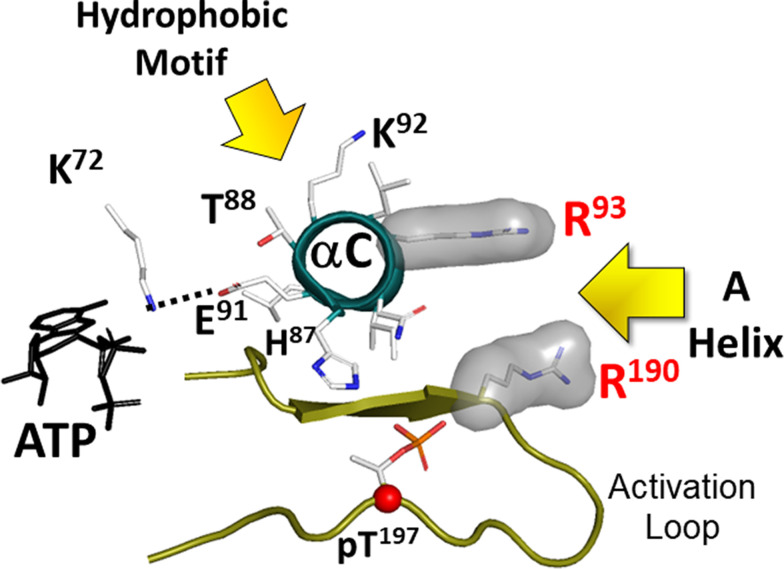
Two conserved hydrophobic pockets anchor the C-helix in its active conformation. The two hydrophobic anchors to the N-lobe come from the A-helix (residues F26 and W30/FxxxW motif) and from the Ct-tail (HF motif). By filling the space between the N-lobe and the C-lobe, the FxxxW motif stabilizes the closed conformation in PKA. In the active phosphorylated C-subunit the hydrophobic pocket is lined by Arg93 in the C-helix of the N-lobe and Arg190 in the activation loop of the C-lobe. The HF motif is anchored to Lys92 in the C-helix. These two motifs keep the C-Helix in an αC-IN position, which is a characteristic feature of active kinases (Taylor and Kornev, TIBS 2011). Glu91 is a conserved residue in the C-helix of all kinases. It reaches across to another conserved residue, Lys72 in β3 strand. Together these residues stabilize the α- and β-phosphates of ATP, positioning the γ-phosphate for transfer.