FIG 2.
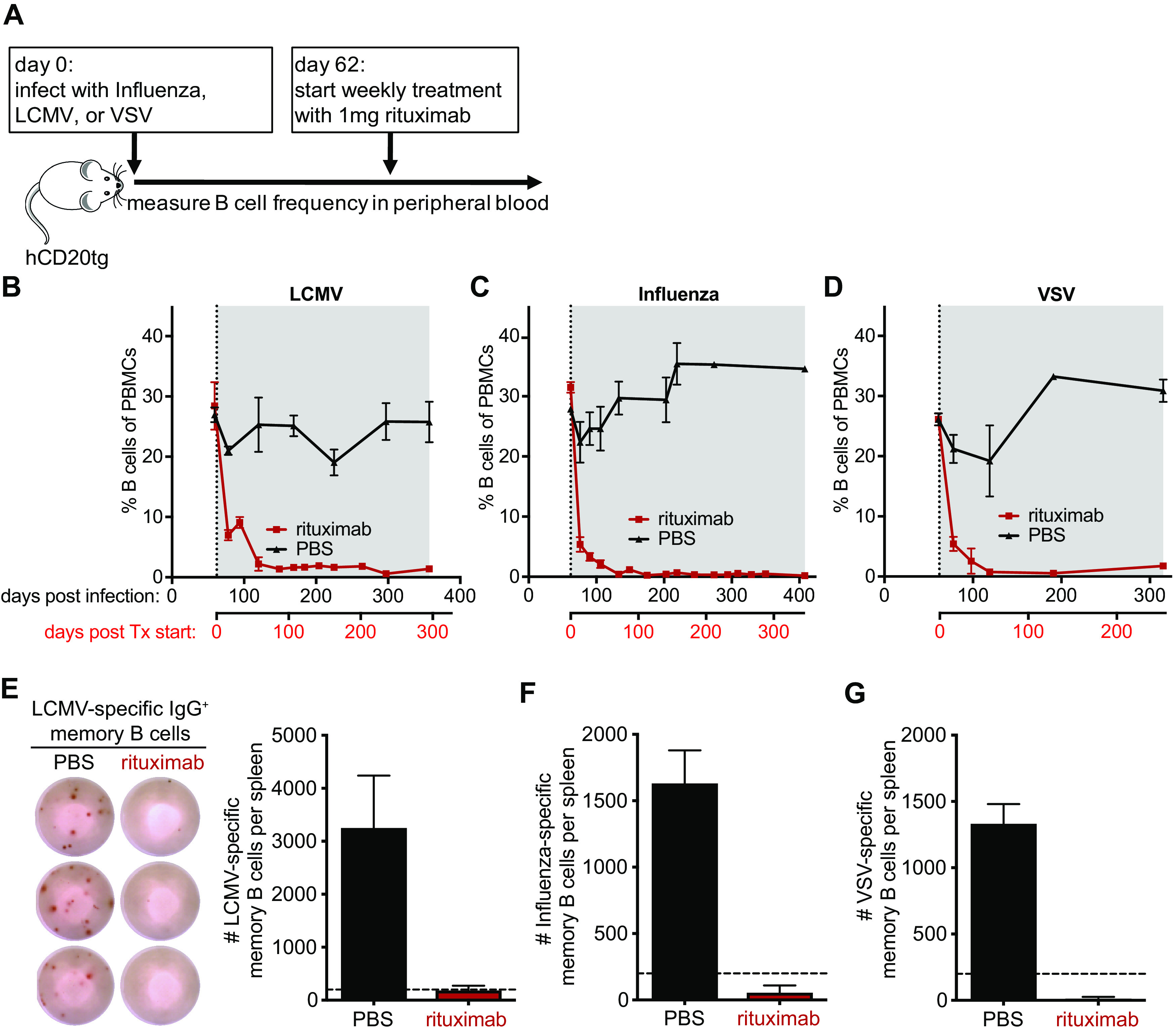
Efficient depletion of B cells in hCD20tg mice by rituximab. hCD20tg mice were infected with influenza virus, LCMV, or VSV, and weekly treatment with rituximab (red) or PBS (black) was initiated on day 62 postinfection. (A) Experimental design. (B to D) The frequency of B cells (B220+ CD19+ CD3−) among peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was monitored by flow cytometry at the indicated times after infection with LCMV (B), Influenza (C), or VSV (D). Treatment initiation and period are indicated by vertical dotted lines and gray shading, respectively. (E) Representative ELISPOT shows LCMV-specific IgG+ memory B cells in the spleen of LCMV immune mice 295 days after treatment initiation with either rituximab or PBS. Graph shows the total number of LCMV-specific IgG+ memory B cells in the spleen. Dotted line indicates the limit of detection. (F and G) Graphs show the total number of Influenza-specific (F) and VSV-specific (G) IgG+ memory B cells in the spleen at the end of the treatment period. Dotted horizontal lines indicate the limit of detection. Data (mean and SEM) from a representative experiment (n = 2 to 6 mice per group) are shown.
