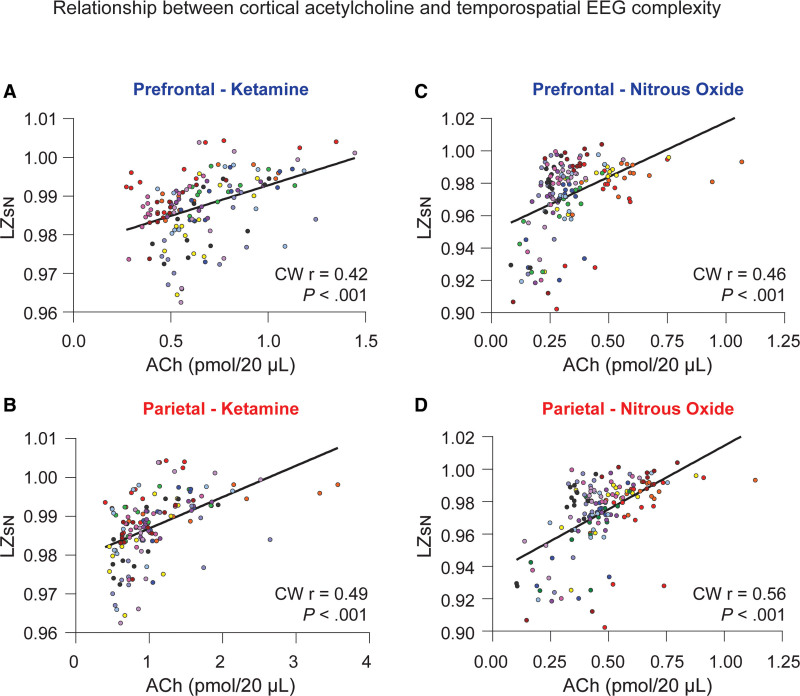
Figure 4.
Relationship between cortical acetylcholine and temporospatial EEG complexity. Changes in prefrontal and parietal acetylcholine levels were significantly correlated with changes in temporospatial EEG complexity in the subanesthetic ketamine infusion (A and B) and nitrous oxide exposure (C and D) cohorts. The data for each subject are displayed by colored dots, with each color corresponding to a single subject across all epochs. To account for clustering of the data within each rat, we calculated the cluster-weighted marginal correlation. The line represents points of best fit. ACh indicates acetylcholine; CW r, cluster-weighted marginal correlation; EEG, electroencephalogram; LZsN, normalized Lempel-Ziv complexity.