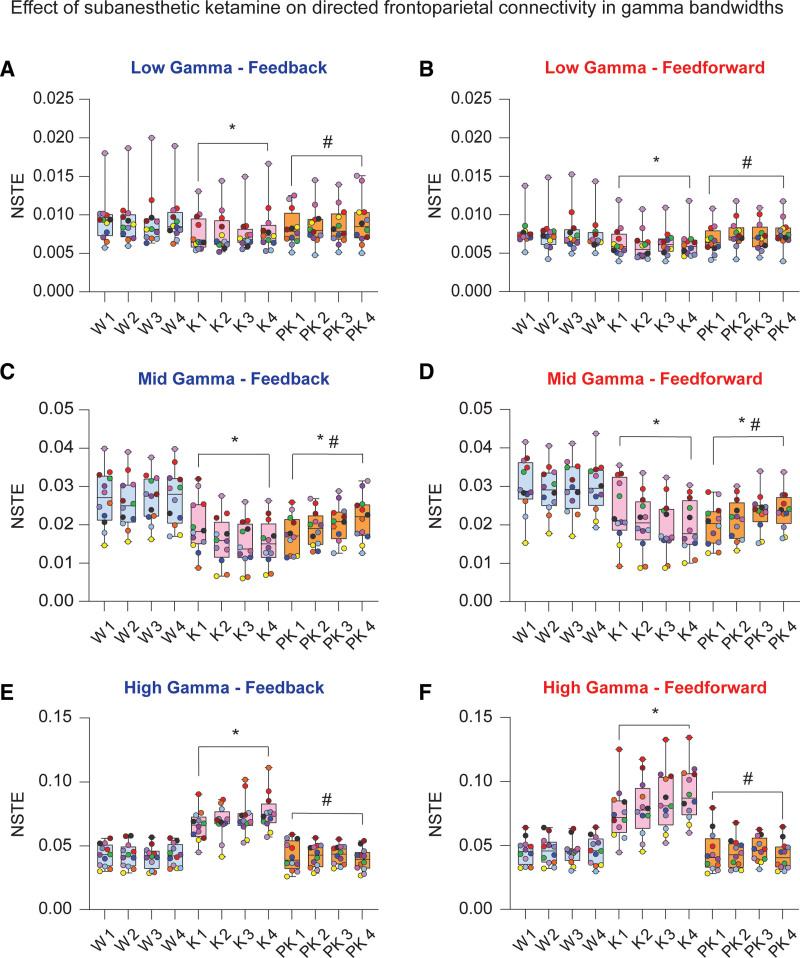
Figure 5.
Effect of subanesthetic ketamine infusion on directed frontoparietal connectivity in gamma bandwidths. Subanesthetic ketamine infusion significantly decreased frontoparietal connectivity in the low gamma bandwidth (25–55 Hz) in both feedback and feedforward directions relative to baseline wake state (A and B). Frontoparietal connectivity in the mid gamma bandwidth (85–125 Hz) decreased in feedback and feedforward directions during subanesthetic ketamine and remained depressed relative to baseline wakefulness during postketamine recovery (C and D). Feedback and feedforward connectivities between frontal and parietal cortices were significantly increased in the high gamma bandwidth (125–175 Hz) during subanesthetic ketamine treatment, returning to levels comparable to baseline wakefulness during postketamine recovery (E and F). A linear mixed model with a random intercept for each rat was used for statistical comparisons. Post hoc pairwise tests between states were performed with single-step correction for multiple comparisons via Tukey test. The box plots show the median (horizontal bar) and interquartile range for averaged data over all 12 subjects at each epoch. The whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values within each epoch. The data for each subject are displayed by colored dots, with each color corresponding to a single subject across all epochs. *Significant compared to wake. #Significant compared to subanesthetic ketamine infusion. The statistical comparisons are shown at P < .05. The exact P values are provided in the text in the Results section. The mean, SD, and F statistics for statistical comparisons are provided in Supplemental Digital Content, Table 5, http://links.lww.com/AA/D757. K indicates subanesthetic ketamine infusion; NSTE, normalized symbolic transfer entropy; PK, postketamine recovery; SD, standard deviation; W, wake.