Figure 4.
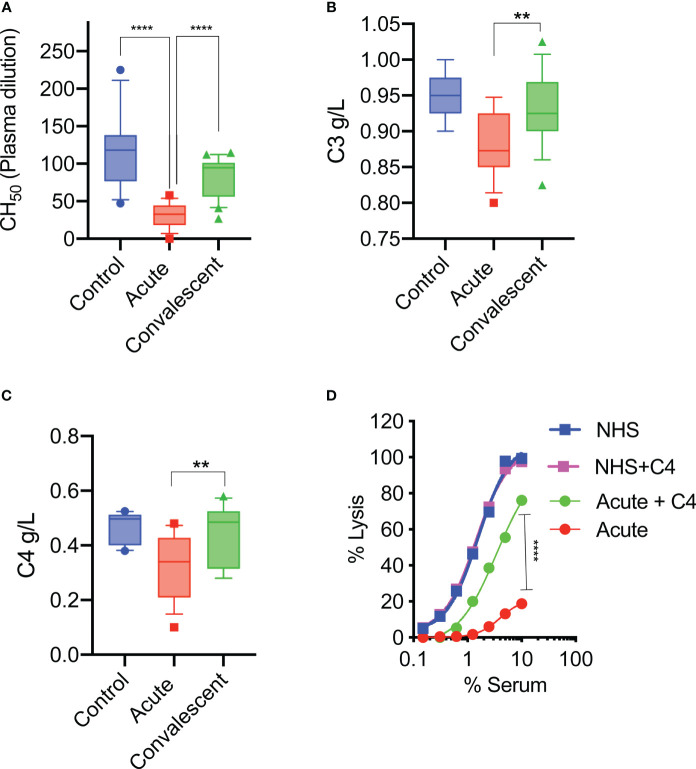
At hospital admission, sera of severely ill COVID-19 patients lack complement functional activity. Sheep RBCs were coated with anti-sheep erythrocyte antibodies and incubated with different serum concentrations. The serum dilution required to lyse 50% of RBCs (CH50) was calculated. The haemolytic activity of sera from acute COVID-19 patients (n= 25) is significantly impaired compared to sera from the same patients after recovery or to those of control NHS (n=14) (A). Serum levels of complement C3 and C4 were also significantly lower in acute sera compared to convalescent sera and control sera (NHS) (B, C). Results were analysed using 1-way ANOVA, with Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons. ****p < 0.0001, **p < 0.01. Reconstitution of sera taken during the acute phase of severe COVID-19 with 10 μg/mL of purified C4 restored the deficient haemolytic activity (D). Results were analysed using 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test.