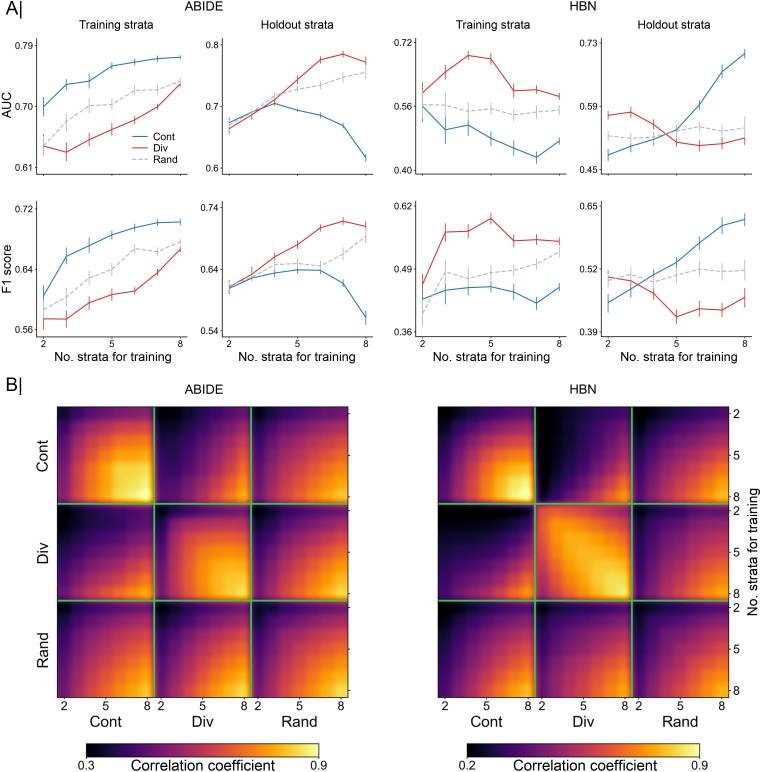
Fig 2. Accuracy of out-of-distribution prediction and consistency of extracted predictive patterns.
Results are based on the classification of ASD versus TD using functional connectivity profiles. (A) Comparison of model accuracy based on contiguous (Cont) and diverse (Div) training sets in the classification of autism. Prediction performance is reported as AUC (top) and F1 score (bottom) in 2 separate cohorts: ABIDE (left) and HBN (right). Accuracy is assessed using different training sets sized from 2 to 8 combined strata. For each cohort, the first column indicates the prediction accuracy using a 10-fold CV strategy based solely on participants from the training strata. Folds were randomly sampled, without considering the propensity scores of the participants. The second column displays the performance in the holdout strata, which contains the remaining participants (from untouched strata). As a baseline for comparison, we used an additional sampling scheme (Rand): Participants for the training set were randomly chosen regardless of their propensity scores. (B) Consistency of model coefficients was quantified by Pearson correlation coefficient across 2 given models in the contiguous, diverse, and random data scenarios. For each of these sampling schemes, consistency is shown for different numbers of combined strata used for predictive model training (from 2 to 8 combined strata), delineated by the green segments. Building models based on diverse strata of participants entailed considerable differences in predictive patterns from those learned based on models with similar participants (i.e., contiguous). Data underlying this figure can be found in S1 Data. ABIDE, Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; AUC, area under the curve; CV, cross-validation; HBN, Healthy Brain Network; TD, typically developing.