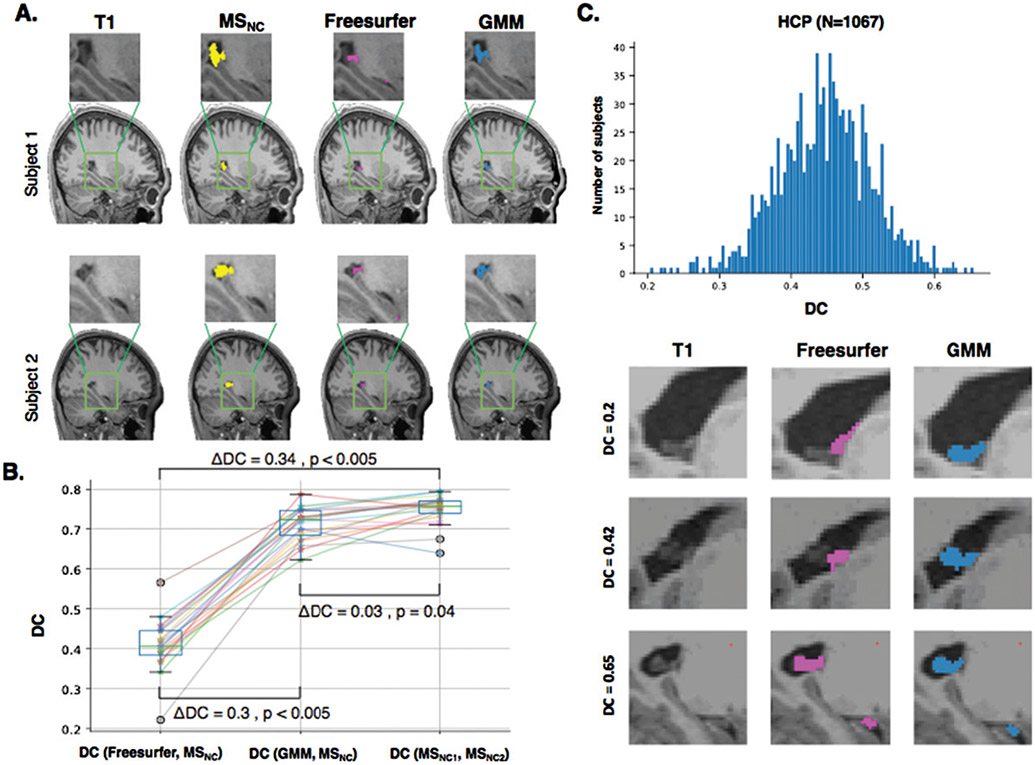
Fig. 3.
ChP segmentation in the HCP dataset. A) ChP was segmented on T1-weighted MRIs without contrast in 20 participants of HCP dataset using manual (MSNC) as well as automatic Freesurfer and GMM segmentations. B) We computed DC to measure similarity between Freesurfer and MSNC, and GMM and MSNC. We also measured DC between MSNC1 and MSNC2 (i.e., segmentations performed by first and second researchers) as the highest level of agreement obtained by MS. GMM significantly improved Freesurfer segmentation (ΔDC=0.3, p < 0.005) and reached close to accuracy of MS (ΔDC=−0.03, p < 0.04). C) GMM and Freesurfer segmentations were performed for 1067 subjects of HCP dataset. The histogram shows the DC similarity between GMM and Freesurfer. GMM and Freesurfer segmentations for three subjects with low similarity (DC = 0.2), medium similarity (DC = 0.42) and high similarity (DC = 0.65). MSC, manual segmentations performed on T1-weighted MRIs with contrast; MSNC, manual segmentations performed on T1-weighted MRIs with no contrast; GMM, Gaussian Mixture Model; DC, dice coefficient; ChP, choroid plexus; HCP, Human Connectome Project.