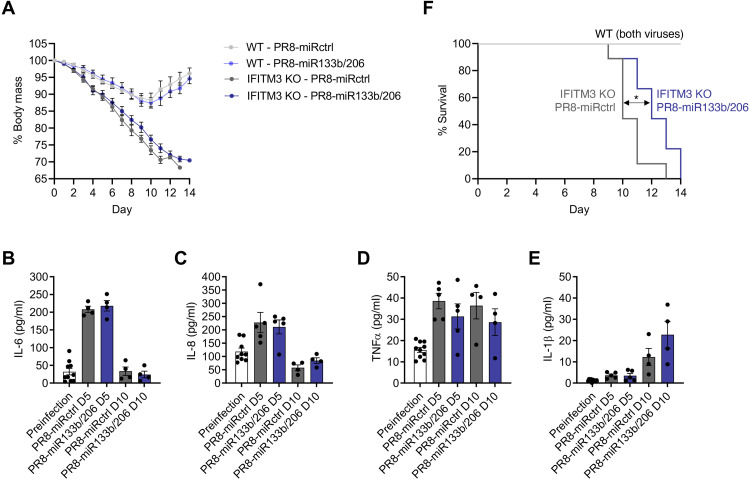
Fig. 2. Attenuation of influenza virus cardiac infection does not significantly alter morbidity but decreases mean survival time in IFITM3 KO mice.
(A) WT and IFITM3 KO mice were intranasally infected with PR8-miR133b/206 or PR8-miRctrl (50 TCID50) and monitored daily for weight loss. Points depict mean values collected from at least three experiments, and error bars represent SD of the mean. Differences between WT and KO mouse weights were significant from day 4 onward with P < 0.05 by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Differences in weight loss when comparing PR8-miRctrl and PR8-miR133b/206 within the individual mouse genotypes were not significant. (B to E) A separate cohort of IFITM3 KO mice was infected with PR8-miR133b/206 or PR8-miRctrl (50 TCID50). Serum was collected before infection and at days 5 and 10 after infection for multiplex quantification of (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, (D) TNFα, and (E) IL-1β. Data points represent individual mice, and bars represent mean values. Error bars depict SD of the mean. Comparisons were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. No statistically significant differences were observed between the two viruses at either time point. (F) Survival curves of mice as infected in (A). The indicated P value is for statistical comparison of the IFITM3 KO survival curves (shown by double arrow) as calculated using a Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test.