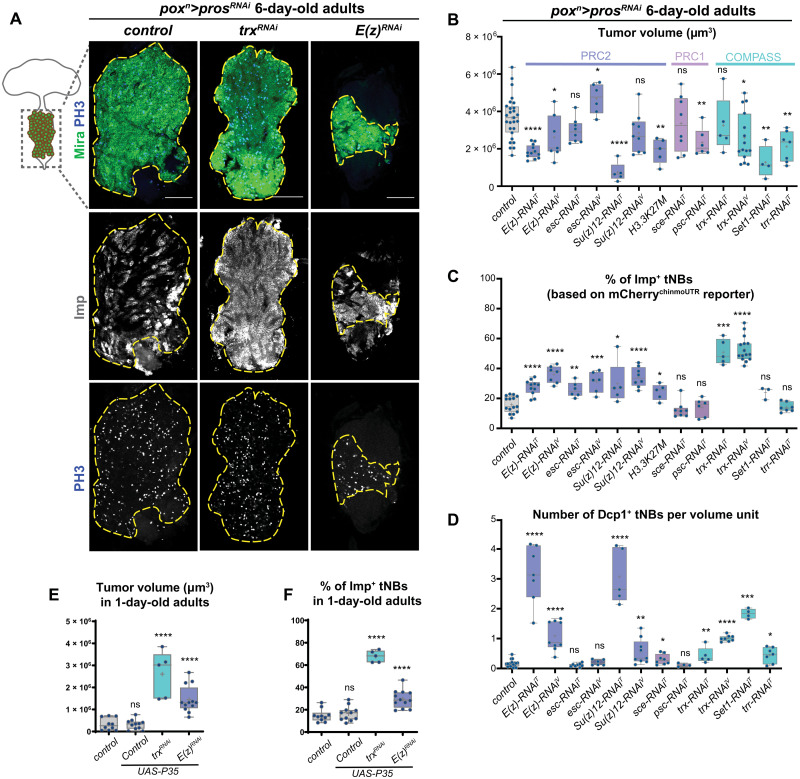
Fig. 2. Knockdown of COMPASS and Polycomb-Group genes in poxn>prosRNAi NB tumors.
(A) Control poxn>prosRNAi tumors or poxn>prosRNAi tumors with RNAi-mediated inactivation of E(z) and trx. Immunostainings against Mira (green) label all tNBs. Immunostainings against Imp (red) label the subpopulation of Imp+ tNBs. Immunostaining against PH3 (phosphorylated Histone 3) labels mitotic cells. Scale bars, 100 μm. The dashed lines delimit the area of the tumor in the VNC of 6-day-old adults. Images are single confocal sections. (B to D) Box plots recapitulating quantifications of tumor volumes, proportions of Imp+ tNBs, and the number of apoptotic cells for poxn>prosRNAi control tumors compared to poxn>prosRNAi tumors with the additional RNAi-mediated knockdown of various members of the PcG and COMPASS complexes. Asterisks above plots indicate statistically significant P values for assessing difference with control tumors. All measurements are made in tumors that persist in 6-day-old adults. In (C), Imp+ tNBs are identified using the mCherrychinmoUTR reporter construct (see also fig. S2). In (D), apoptotic cells are labeled with an anti-Dcp1 antibody. Apoptotic cells are quantified per unit of volume (1 unit = 10,000 μm3). T in uppercase indicates RNAi lines from the Transgenic RNAi Project (TRiP) provided by the Bloomington Stock Center, while V in uppercase indicates RNAi lines from the Vienna Drosophila Resource Center (VDRC). (E and F) Box plots indicating tumor volumes (E) and the proportions of Imp+ tNBs (F) for poxn>prosRNAi control tumors compared to poxn>prosRNAi, p35; poxn>prosRNAi, p35, trxRNAi; and poxn>prosRNAi, p35, E(z)RNAi tumors in the VNC of 1-day-old adults. ns, not significant.