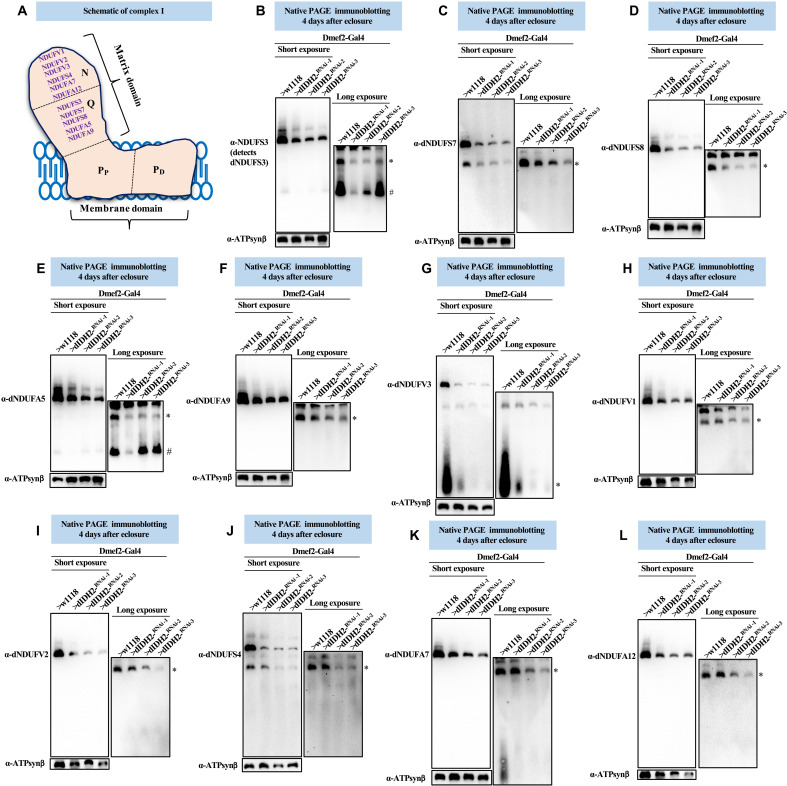
Fig. 4. The synthesis of matrix-localized CI AIs is impaired when dIDH2 is disrupted.
(A) Illustration of mitochondrial CI depicting the approximate positions of the N-, Q-, PP-, and PD-modules. A commercially available antibody that detects dNDUFS3 and antibodies we raised against dNDUFA5, dNDUFA9, dNDUFS7, and dNDUFS8 were used to examine the biogenesis of the Q-module. Biogenesis of the N-module was tracked by immunoblotting with antibodies we raised against dNDUFS4, dNDUFA7, dNDUFA12, dNDUFV1, dNDUFV2, and dNDUFV3. (B to L) Mitochondrial preparations from flight muscles dissected from flies with the genotypes shown were analyzed by BN-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated. The blots were imaged following a short exposure to detect the holoenzyme and supercomplexes, after which the region corresponding to the holoenzyme and supercomplexes was cut off, and the rest of the blot was reimaged after a longer exposure to detect the AIs. The antibodies used were anti-NDUFS3 that detects dNDUFS3 (B), anti-dNDUFS7 (C), anti-dNDUFS8 (D), dNDUFA5 (E), anti-dNDUFA9 (F), anti-dNDUFV3 (G), anti-dNDUFV1 (H), anti-dNDUFV2 (I), anti-dNDUFS4 (J), anti-dNDUFA7 (K), and anti-dNDUFA12 (L). Anti–ATP synthase, subunit B (ATP5F1B), which detects the Drosophila ortholog, dATP-Synβ, was used as a loading control. # refers to the initiating AI of the Q-module, and other AIs are denoted as *. AIs denoted with # and * were quantified. See figs. S5 to S7 for replicates and quantification of immunoblots.