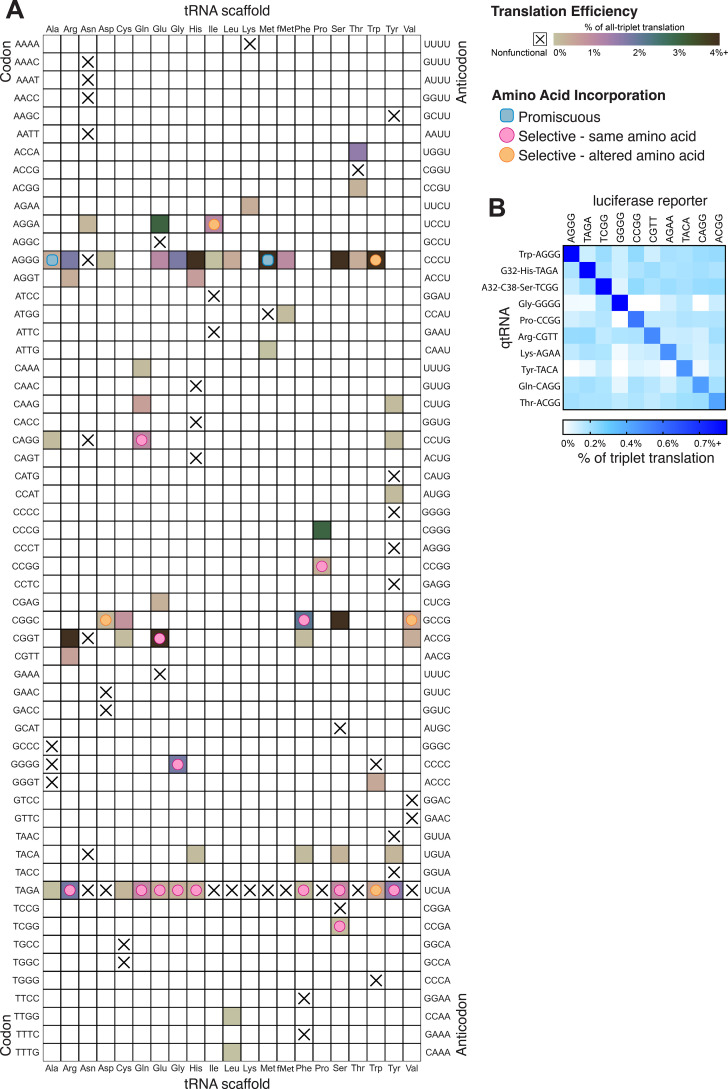
Figure 6. Compiled qtRNA measurements.
(A) Compiled results of quantifying quadruplet tRNAs (qtRNA) translation efficiency (Materials and methods, ‘Luciferase readthrough assay’) and charging (Materials and methods, ‘Quantification of qtRNA charging using mass spectrometry’). The qtRNA scaffold (columns) and codon (rows) are indicated. The translation efficiency is indicated on each qtRNA that could be measured, or marked as ‘nonfunctional’, indicating that the qtRNA exhibits too strong a growth defect to measure, or does not produce a measurable increase luminescence upon induction of qtRNA expression. Translation efficiency is measured as a percent of all-triplet translation (Materials and methods, ‘Luciferase readthrough assay’). fMet qtRNAs are measured with a luciferase reporter bearing a quadruplet codon at residue 1; all others are measured with a quadruplet codon at residue 357 of luxAB. Charging results are indicated on the table for qtRNAs derived from each scaffold-codon pair; the measured qtRNAs may contain additional mutations; see Supplementary files 2 and 3. Data represent the mean of three to eight technical replicates in each of between one and eight biological replicates. For complete compiled raw data, see Figure 6—source data 1. (B) A miniature all-quadruplet genetic code. For each of the 10 qtRNAs (rows), we measured readthrough of a luciferase transcript containing the indicated quadruplet codon at residue 357 (columns). For raw data, see Figure 6—source data 2.