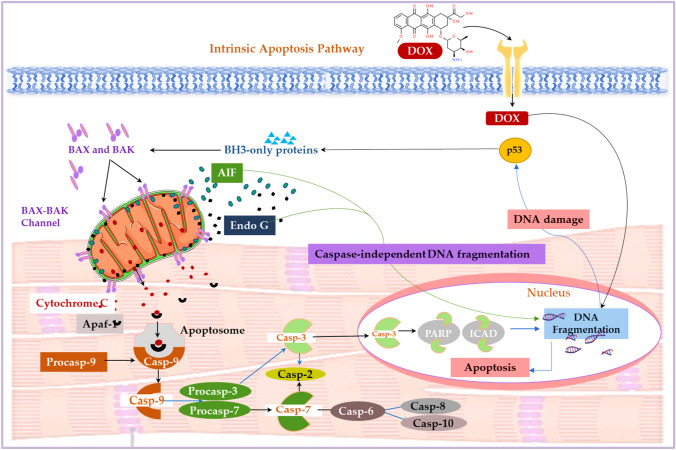
Fig. 5.
Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway. The release of cytochrome c, via mitochondrial dysfunction, mediates the oligomerization of apoptosis-protease activating factor-1 (Apaf-1), generating the apoptosome, which activates Casp-9 to cleave the executioner Casp-3/7. Activated Casp-3, but not Casp-7, is then translocated to the nucleus where it cleaves the inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase (CAD) to induce DNA fragmentation. Furthermore, the loss in mitochondrial potential via Dox treatment, stimulates the release of mitochondrial-bound pro-apoptotic proteins, endonuclease G (EndoG) and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) which are then translocated to the nucleus to induce caspase-independent DNA fragmentation and genomic instability. These processes accelerate cardiomyocyte death via dysregulated apoptosis