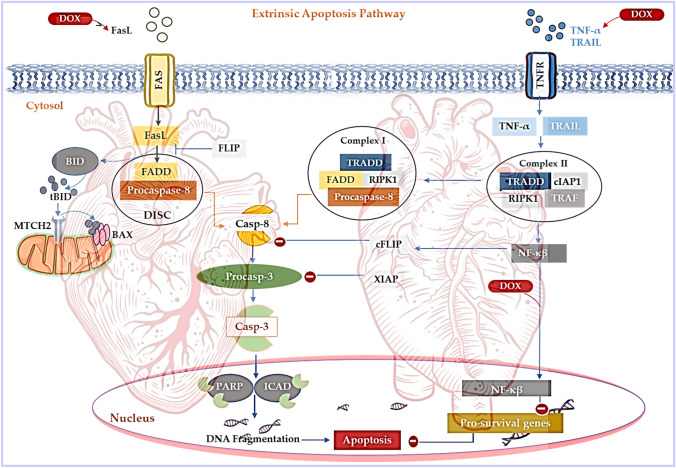
Fig. 6.
Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via the extrinsic pathway. The extrinsic pathway is regulated by the death receptors (Fas, the TNF receptor superfamily 1A (TNFR1), TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptors 10a (TRAIL1) and TRAIL2 (10b)) which are overstimulated during Dox exposure. The death-inducing signaling complex (DISC), “complexes I and II”, is formulated by the assembly of dynamic multi-proteins, that operate as molecular platforms that regulate Casp-8. Activated Casp-8 facilitates the proteolytic maturation of executioner Casp-3/6/7 which drives apoptosis via DNA damage. Simultaneously, Dox-mediated cleavage of pro-apoptotic BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID) forms truncated BID (tBID). The tBID is then translocated to the outer mitochondrial membrane via a Fas-dependent pathway, which is reliant on the binding of modulator of apoptosis 1 (MOAP1) to the BID receptor mitochondrial carrier 2 (MTCH2). Dox also mediates the reduction of cFLIPs and XIAP via NF-κβ overexpression to trigger the onset and progression of apoptosis