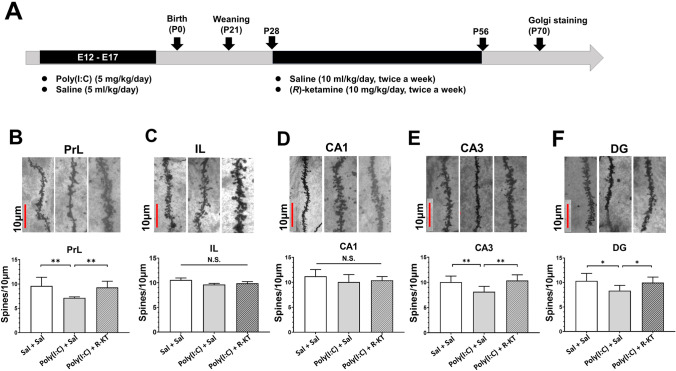
Fig. 3.
Effects of (R)-ketamine on dendritic spine density in the brain of adult offspring after prenatal poly(I:C) exposure. A Schedule of treatment and behavioral tests. Saline (5.0 ml/kg/day) or poly(I:C) (5.0 mg/kg/day from E12 to E17) was injected i.p. into pregnant mice. Male offspring was separated from mothers on P21. Saline (10 ml/kg/day, twice a week) or (R)-ketamine (10 mg/kg/day, twice a week) was administered i.p. to male offspring from P28 to P56. Brain samples for Golgi staining were collected at P70. B–F Representative images of Golgi staining in the mPFC and hippocampus of adult offspring after MIA. The number of dendritic spine density in the PrL of mPFC, CA3, and DG of poly(I:C) + saline-treated group was significantly lower than that of the other two groups. In contrast, there were no changes for spine density in the PL and CA1 among the three groups. *P < 0.05, compared with poly(I:C) + saline group. **P < 0.01, compared with poly(I:C) + saline group. N.S.: not significance. The value is expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 8)