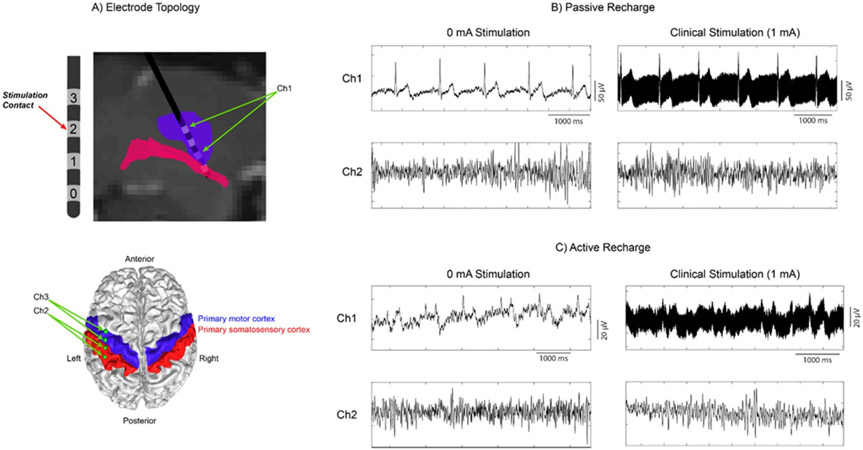
Figure 6.
ECG and high frequency stimulation artifacts during concurrent stimulation and sensing with the bidirectional neural interface (Sumit RC + S, Medtronic) in a patient with ET. (a) Electrode placement within the VIM, and cortical strip placement over the primary motor/somatosensory cortices (Ch1 subcortical channel and Ch2, Ch3 cortical channels). (b) Recording during passive recharge at 0 mA and clinical stimulation levels, at Ch1 (subcortical channel) and Ch2 (cortical channel). Passive recharge utilizes a square pulse followed by a long-term small-amplitude charge in the opposite polarity. (c) Recording during active recharge using the same amplitudes and channels as (b). Active recharge sends sequential symmetric square pulses with opposite polarities, balancing the charge in a shorter time period.