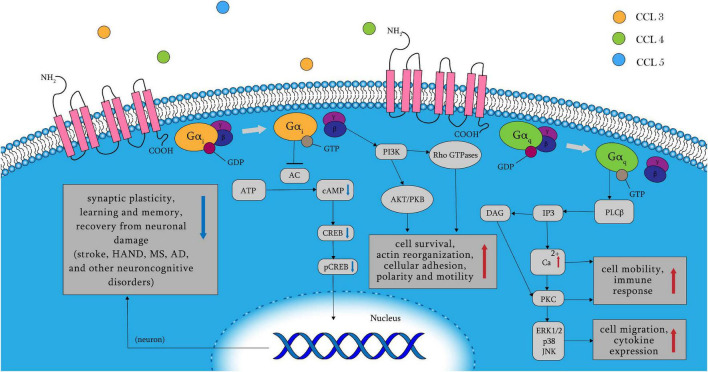
FIGURE 1.
CCR5 receptor signaling pathways. When the amino terminus of CCR5 binds to its ligand, its following signaling pathway is mainly controlled by Gαq, Gαi, and βγ subunits. The Gαi pathway results in the release of intracellular Ca2+ and decreased learning and memory function, as well as worsened recovery from neuronal damage by reduced cAMP and pCREB. Activation of Gαq results in cell migration and cytokine expression in immune response. And the βγ subunits leads to cell survival, adhesion and motility through multiple following signaling pathways such as AKT/PKB and Rho GTPase. AC, adenylyl cyclase; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; AKT/PKB, protein kinase B; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CCR5, C–C chemokine receptor 5; CREB, cAMP-response-element binding protein; DAG, diacylglycerol; HAND, HIV-related neurocognitive disorders; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; JNK, C-Jun N-terminal kinases; MS, multiple sclerosis; pCREB, phosphorylated cAMP-response-element binding protein; PKB/Akt, protein kinase B; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C.