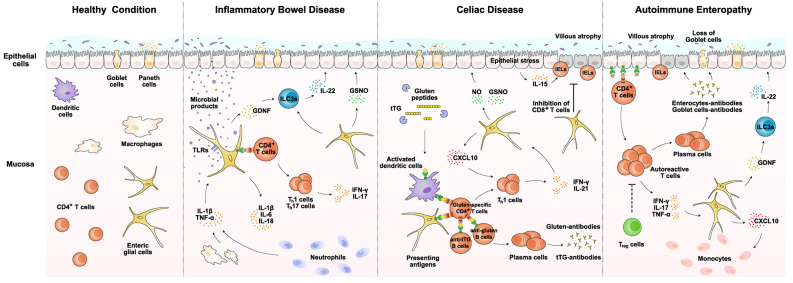
Figure 2.
EGCs in immunological disorders of the gut. EGCs exert potential roles in several important immunological disorders of the gut, including inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and autoimmune enteropathy. EGCs could directly sense invading pathogens via specific TLRs and release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-6. Also, EGCs are able to produce CXCL10 and facilitate the recruitment of lymphocytes or monocytes. In addition, EGCs may present disease-related antigens via MHC-II to CD4+ T cells. Moreover, EGCs would produce GDNF and GSNO that indirectly or directly modulate the epithelial integrity. Details of the immune functions of EGCs are described in the main text. Notably, different subtypes of EGCs are not particularly distinguished for immune functions in this diagram. GDNF, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; GSNO, S-nitrosoglutathione; IELs, intraepithelial lymphocytes; ILC3s, type 3 innate lymphoid cells; NO, nitro oxide; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; tTG, tissue transglutaminase.