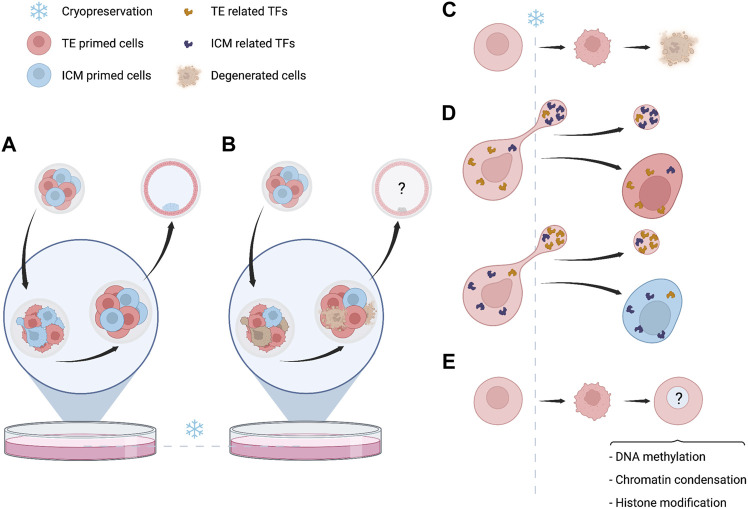
FIGURE 2.
Events related to embryo cryopreservation with potential developmental consequences. (A) Full recovery of embryo viability without evident changes in morphology or organization. (B) Difference in survival rates between embryonic cells can lead to variation in the proportion of cells primed towards trophectoderm (TE) or inner cell mass (ICM). The question marks refer to unknown consequences for further embryo viability and/or cell lineage establishment. (C) Degeneration of cells is a common morphological evidence of damage induced by cryopreservation. If few cells are damaged, embryos still can survive, implant and successfully result in pregnancy and live-birth. The effect of this loss of material is still unknown. (D) During cleavage cytoplasmic material is transiently released and subsequently reabsorbed. The causes of this phenomenon are unknown and probably stochastic, also the biological significancy of these projections is unknown. However, if interrupted by cryopreservation, a potential modification of the cytoplasmic content can be hypothetically considered. (E) Even if complete survival of blastomeres is reached, which is more common with modern vitrification methods, some changes over different epigenetic layers may still persist and must be considered.