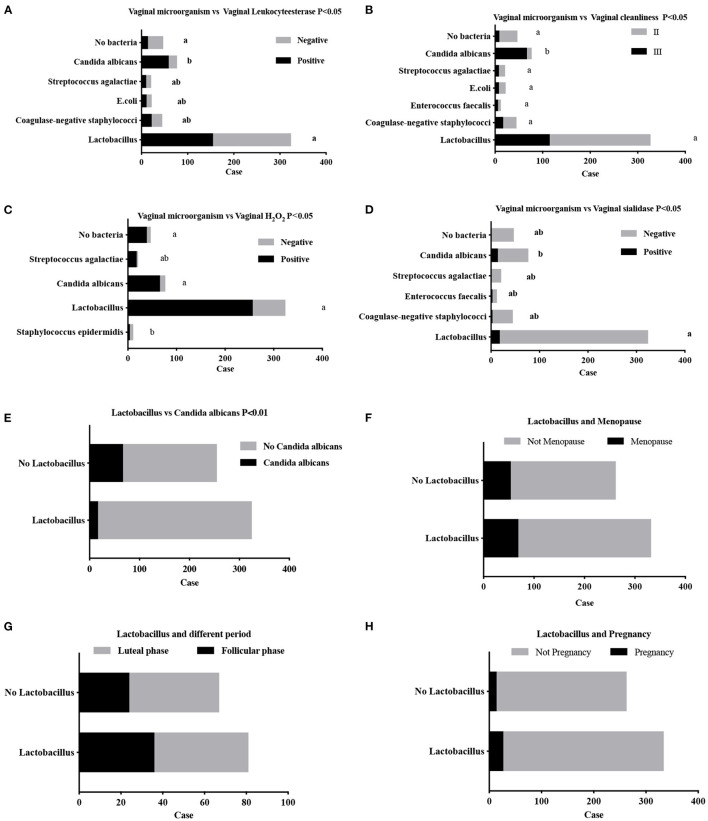
Figure 4.
Distribution of vaginal microorganisms in premenopausal and postmenopausal women using general bacterial culture techniques. (A,B) Vaginal secretion triple test: Candida albicans, the dominant bacterial population related to a higher positive rate of leukocyte esterase (A) and poorer cleanliness (B). Staphylococcus epidermidis, the main bacterial population, was related to decreased hydrogen peroxide content (C), a higher sialidase content existed in the Enterococcus faecalis population (D). Women carrying Lactobacillus as the primary bacterial population were less susceptible to certain pathogens, such as Candida albicans (E). There was no significant difference in lactobacillus as the dominant bacteria between the premenopausal and postmenopausal groups (F). There was also no significant difference in Lactobacillus, as the dominant bacteria, distribution in different phases of the menstrual cycle (G). Among them, Lactobacillus dominated 65.9% (27/41) in pregnant women and 55.22% (307/556) of non-pregnant women (H).