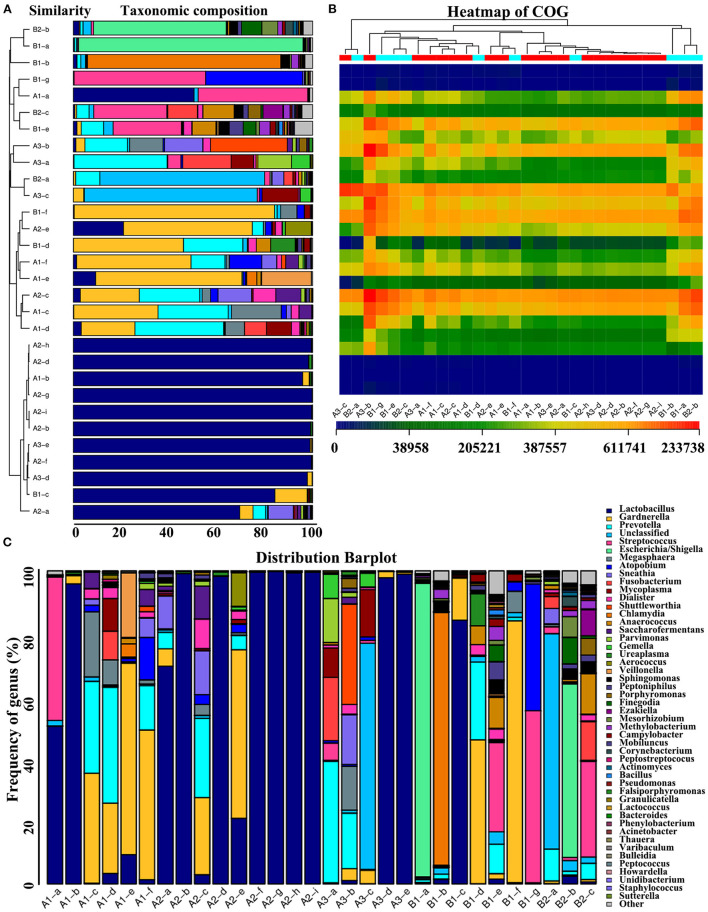
Figure 5.
Community taxonomy system at the genus level and COG-based functional structure distribution. (A) Taxonomic composition distribution graph showing the relative sample microorganism classification abundance. The horizontal or vertical axis is the sample number or relative abundance ratio. The width of different colors indicates the relative abundance ratio of different species at the taxonomic level. Left panel: Bray-Curtis-based sample clustering tree diagram; middle panel part: Histogram of species abundance of clustering order; right panel: Illustration of the species. (B) A functional abundance heat map based on COG was drawn using the functional abundance matrix. Each column represents a sample, the row represents the function, and the color block represents the functional abundance value. The redder the color is, the higher the abundance, and the more blue the color is, and the lower the distance. Samples from the same group have the same color. Sample distance is represented by the length of the branches. The more similar the samples are, the closer the branches of the same color in the figure are from the same group. (A) RNA processing and modification; (B) Chromatin structure and dynamics; (C) Energy production and conversion; (D) Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; (E) Amino acid transport and metabolism; (F) Nucleotide transport and metabolism; (G) Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; (H) Coenzyme transport and metabolism; (I) Lipid transport and metabolism; (J) Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; (K) Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; (L) Transcription; (M) Replication, recombination and repair; (N) Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; (O) Cell motility; (P) Post-translational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones; (Q) Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism; (R) General function prediction only; (S) Function unknown; (T) Signal transduction mechanisms; (U) Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; (V) Defense mechanisms; (W) Extracellular structures; (Y) Nuclear structure; (Z) Cytoskeleton; (C) Distribution bar plot.