Figure 3.
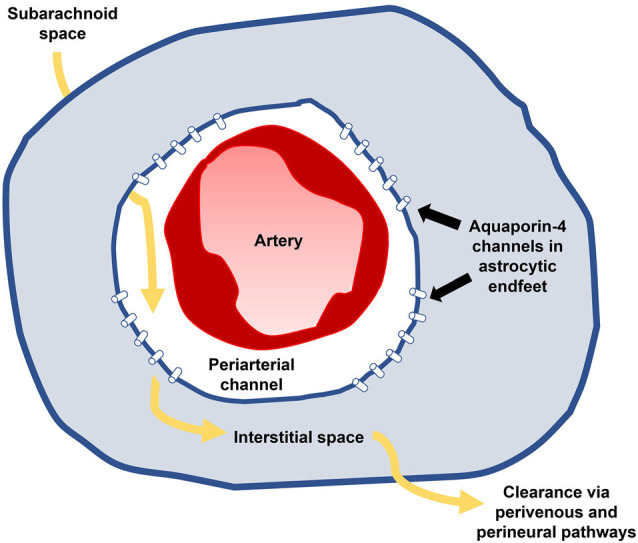
Glymphatic influx (yellow arrows) occurs along periarterial channels within subarachnoid spaces (white) and enters the parenchyma (blue) through aquaporin-4 transporters on astrocytic endfeet. Subarachnoid CSF joins interstitial fluid and passes through the brain, delivering substances to and from the parenchyma before being absorbed along perivenous and perineural channels. Impaired glymphatic circulation may result in part from impaired influx through poor arterial compliance and results in progressive neurotoxicity contributing to iNPH’s clinical manifestations.
