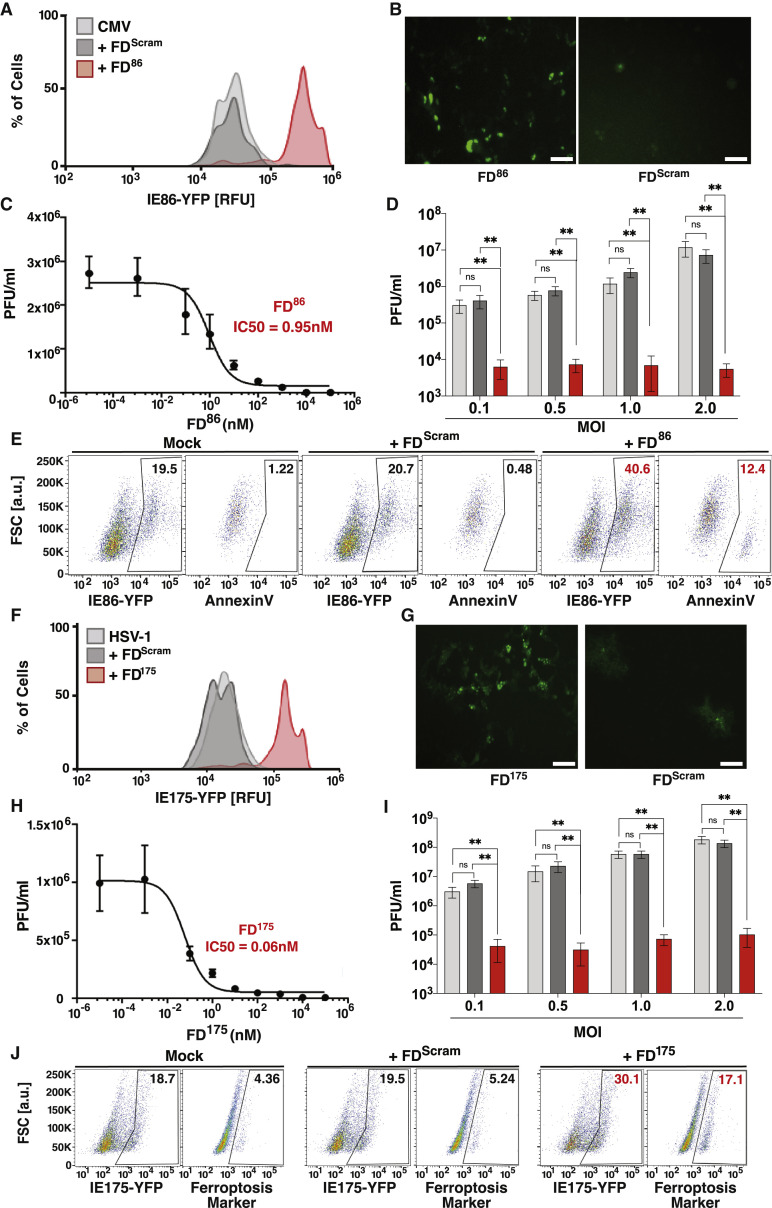
Figure 3.
Open-loop lethality generates an antiviral effect against diverse herpesviruses
(A) Flow cytometry analysis showing that feedback disruption generates IE86 overexpression in CMV-infected cells. ARPE-19 cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD86 or FDScram, then 24 h later infected with CMV (TB40E) encoding an IE86-YFP fusion (MOI = 0.1), and analyzed at 2 days postinfection (dpi).
(B) Micrographs of YFP fluorescence in ARPE-19 cells at 24 h postinfection with TB40E-IE-YFP treated with FD86 or FDScram (MOI = 1.0). Scale bar, 200 μm.
(C) FD86 dose-response curve and corresponding IC50 value. ARPE-19 cells were nucleofected with FD86 at the concentration specified, infected with TB40E-IE86-YFP virus (MOI = 0.1), and virus titered 4 dpi (error bars represent mean ± 1 SD, n = 3 biological replicates).
(D) Antiviral effect of FD86 on CMV. ARPE-19 cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD86 (or mock/FDScram), and 24-h post-nucleofection, cells were infected with TB40E-IE86-YFP virus at different MOIs (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0), and titered at 4 dpi (error bars represent mean ± 1 sd, n = 3 biological replicates).
(E) Apoptosis induction in CMV-infected cells: ARPE-19 cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD86 (or mock/FDScram), 24 h later infected with TB40E-IE86-YFP virus (MOI = 1), and at 48 hpi stained for annexin V and analyzed by flow cytometry.
(F) Feedback disruption leads to IE175 overexpression in HSV-1-infected cells. ARPE-19 cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD175 or FDScram (or mock), then 24 h later infected with HSV-1 (17syn+ strain) encoding an IE175-YFP (MOI = 0.1), and analyzed at 2 dpi.
(G) Micrographs of YFP fluoresence in Vero cells 12 h postinfection with 17syn+ IE175-YFP (MOI = 1.0) and treated with FD175 or FDScram. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(H) FD175 dose-response curve and corresponding IC50 values. Titers were calculated on Vero cells nucleofected with FD175 at the concentration indicated, infected with HSV-1 IE175-YFP (17syn+ strain, MOI = 0.1) 24 h later, and titered 2 dpi (error bars represent mean ± 1 sd, n = 3 biological replicates).
(I) Antiviral effect of FD175 on HSV-1. Vero cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD175 (or mock/FDScram), and 24 h post-nucleofection, cells were infected with HSV-1 (17syn+ strain) at different MOIs (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0), and titered at 4 dpi (error bars represent mean ± 1 SD, n = 3 biological replicates).
(J) Ferroptosis induction in HSV-infected Vero cells. Cells were nucleofected with 25 μM FD175 (or mock/FDScram) and then 24 h later, infected with HSV-1 (17syn+ strain) IE175-YFP (MOI = 1), and at 24-hpi cells, were harvested, stained with a ferroptosis marker (BODIPY C11), and analyzed by flow cytometry. p values derived from Student’s t test: ns, non-significant, ∗∗ < 0.01.
See also Figures S3, S4, and S5.