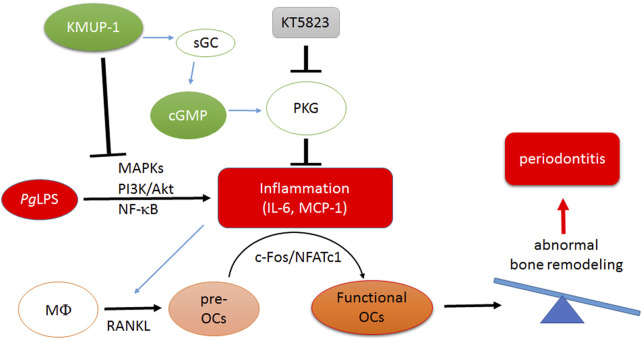
FIGURE 8.
Schematic illustration of molecular mechanism underlying inhibition of PgLPS-induced periodontitis by treatment of KMUP-1. PgLPS triggers pro-inflammatory reactions and thus promotes maturation of osteoclasts. Amplification of osteoclastogenesis leads to imbalance of bone remodeling which aggravates periodontitis progression. KMUP-1, through elevation of the cGMP-PKG pathway and reduction of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, suppresses PgLPS-induced osteoclast differentiation thereby diminishing functional osteoclast maturation.