FIGURE 1.
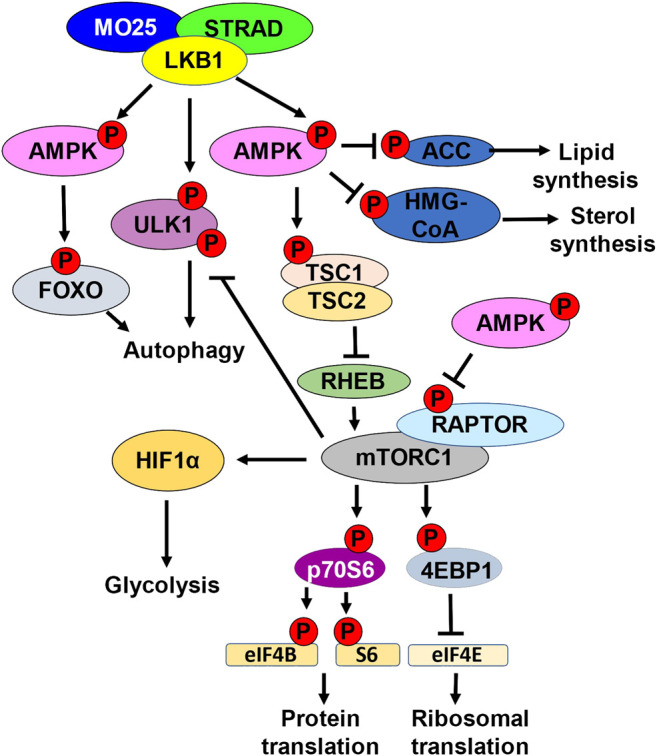
LKB1 metabolic nexus. Schematic representation of downstream LKB1 signaling. LKB1 in complex with STRAD and MO25 phosphorylates and activates AMPK. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits ACC, inhibiting lipid synthesis. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits HMG-CoA, inhibiting sterol synthesis. Active AMPK also regulates autophagy by phosphorylating and activating FOXO. LKB1 can directly promote autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1. LKB1 activation of AMPK also inhibits mTORC1 kinase activation. mTORC1 kinase phosphorylates and activates p70S6. p70S6 phosphorylates and activates eIF4B and S6 kinase, promoting protein translation. mTORC1 also phosphorylates and inhibits 4EBP1, the inhibitor of eIF4E. eIF4e activation leads to increased ribosomal translation. mTORC1 can also inhibits autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1. mTORC1 promotes glycolysis by upregulating HIF1α. AMPK directly inhibits mTORC1 by phosphorylating RAPTOR. AMPK can also indirectly inhibit mTORC1 by phosphorylating and activating TSC1/TSC2. Active TSC1/2 complex inhibits RHEB.
