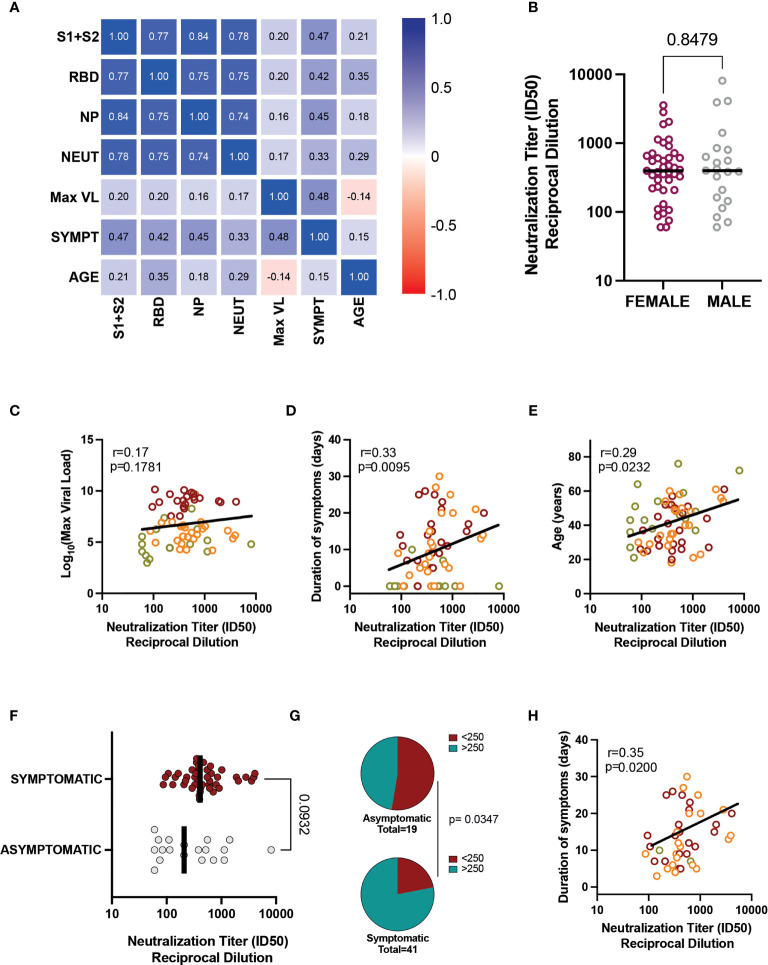
Figure 3.
Associations between humoral responses and clinical/demographic characteristics. (A) Heatmap of correlations between total IgG, neutralizing antibody titer, VL, symptom duration, and age for all patients. (B) Neutralization titers in female and male participants (all groups). Bar indicates median values, and the p-value is shown (Mann-Whitney test). Correlation of neutralization titers with (C) VL, (D) Duration of Symptoms, and (E) Age. Individual values are color-coded: green for Non-early seroconverter individuals at diagnosis, orange for individuals with low viral load, and red for individuals with high viral load. Lines indicate linear regression of all values for illustrative purposes. The correlation coefficient and p-value (Spearman correlation test) are shown. (F) The impact of asymptomatic infection was assessed by comparing neutralizing titers between all asymptomatic (grey dots) and all symptomatic patients (red symbols). (G) Frequency of low and high neutralizers (cutoff value 1/250); the Fisher exact test p-value is shown. (H) Correlation between symptom duration and neutralization titer in symptomatic individuals. The correlation coefficient and p-value (Spearman correlation test) is shown. ID, inhibitory dilution; NP, nucleocapsid protein; RBD, receptor-binding domain; VL, viral load.