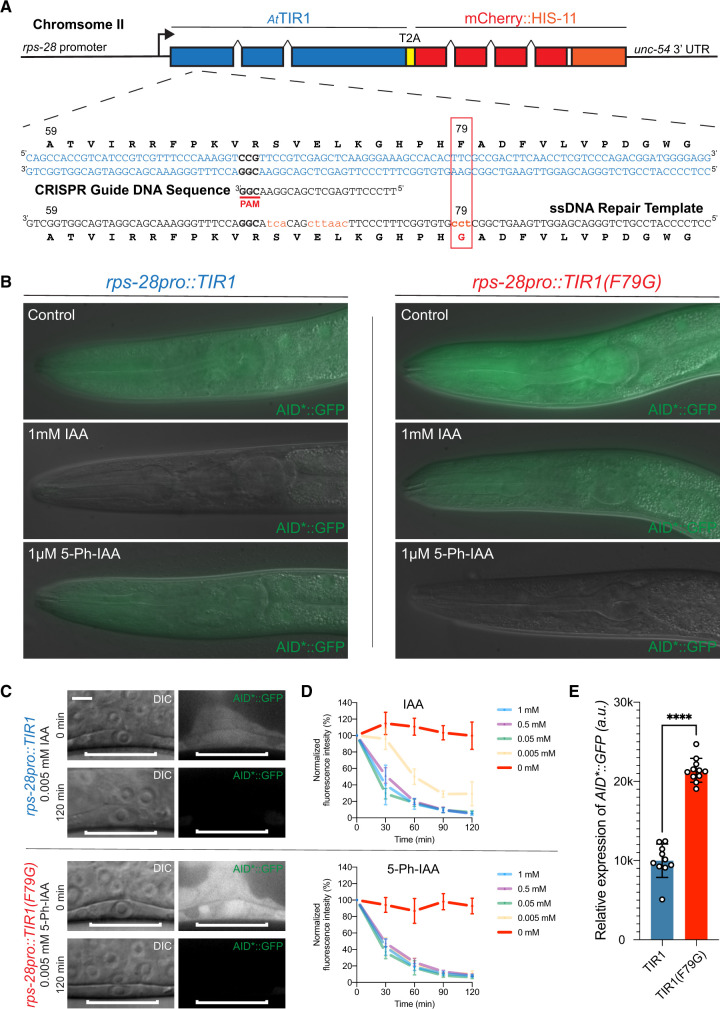
Figure 2.
Mutation of phenylalanine 79 to glycine in the TIR1 protein switches the specificity of the auxin degradation system to one that is now responsive to 5-Ph-IAA. (A) Structure of cshIs128 that encodes both a AtTIR1(WT) protein and an autocatalytically cleaved nuclear-localized mCherry::HIS-11 reporter driven by a ubiquitously expressed ribosomal protein (rps-28) promoter. Below the gene structure is the coding sequence of the region of AtTIR1(WT) that was mutagenized via CRISPR and HDR using a coinjected ssDNA oligo. (B) Representative mid-larval staged animals expressing AID*::GFP and one of two indicated AtTIR1 variants. Animals were grown continuously on untreated NGM plates or NGM plates including the indicated auxin analog at the listed concentration. (C) Micrographs of early L3 staged animals expressing AID*::GFP and one of the two AtTIR1 variants before and 120 min after the addition of the auxin analog. (D) Rates of AID*::GFP degradation were determined by quantifying AID*::GFP in early L3 staged P6.p cells in animals coexpressing the indicated AtTIR1 variant following auxin analog treatment. Data presented as the mean and SD (n ≥ 10 animals examined for each time point). (E) Quantification of the relative expression levels of the AID*::GFP reporter in P6.p cells of early L3 staged animals that were grown on control plates. Data presented as the median with SD (n ≥ 10 animals examined for each TIR1 transgene, and ****P < 0.0001 by a Mann–Whitney U-test).