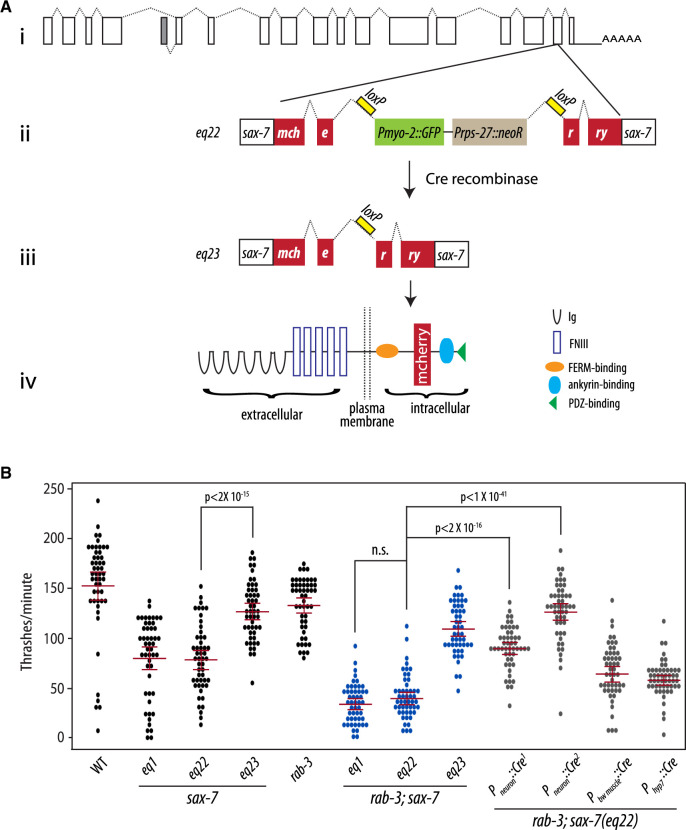
Figure 3.
Neuronal expression of sax-7 rescues rab-3; sax-7 uncoordinated locomotion and neuronal dysfunction. (A) A schematic of the conditional sax-7 knock-in allele, eq22. (i) Gene structure of the sax-7 locus, with boxes representing exons and dotted lines representing introns; the gray box represents an exon used in an alternatively spliced isoform of sax-7 (Chen et al. 2001). eq22 is an in-frame insertion into the penultimate sax-7 exon (ii). The insertion contains mCherry sequence and a gene-disrupting cassette (Pmyo-2::GFP and Prps-27::neoR) that interrupts the mCherry reading frame. This gene-disrupting cassette, which is flanked by loxP sites located in intronic sequences, can be excised out with tissue-specific Cre-recombinase expression (iii) to restore sax-7 expression as (iv) a full-length SAX-7::mCherry fusion protein. Cre-recombinase expression in the germline was used to generate the eq23 allele. (B) Quantitation of thrash rates reveal that eq22 resembles the eq1 null allele and similarly interacts with rab-3 for a synergistically reduced swim rate; in contrast, eq23 does not interact with rab-3. Conditional knock-in of sax-7 in neurons with pan neuronally expressed Cre-recombinase dramatically rescues the low rab-3; sax-7(eq22) thrash rate; in contrast, body-wall muscle or hypodermal knock-in results in modest rescue. Pan neuronally expressed Cre-recombinase, Pneuron::Cre1 and Pneuron::Cre2, was produced using the eqIs4 and tmIs778 transgenes, respectively. The red lines show the mean and the 95% confidence interval. n = 50–75, P-values are shown; n.s., not significant, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test.