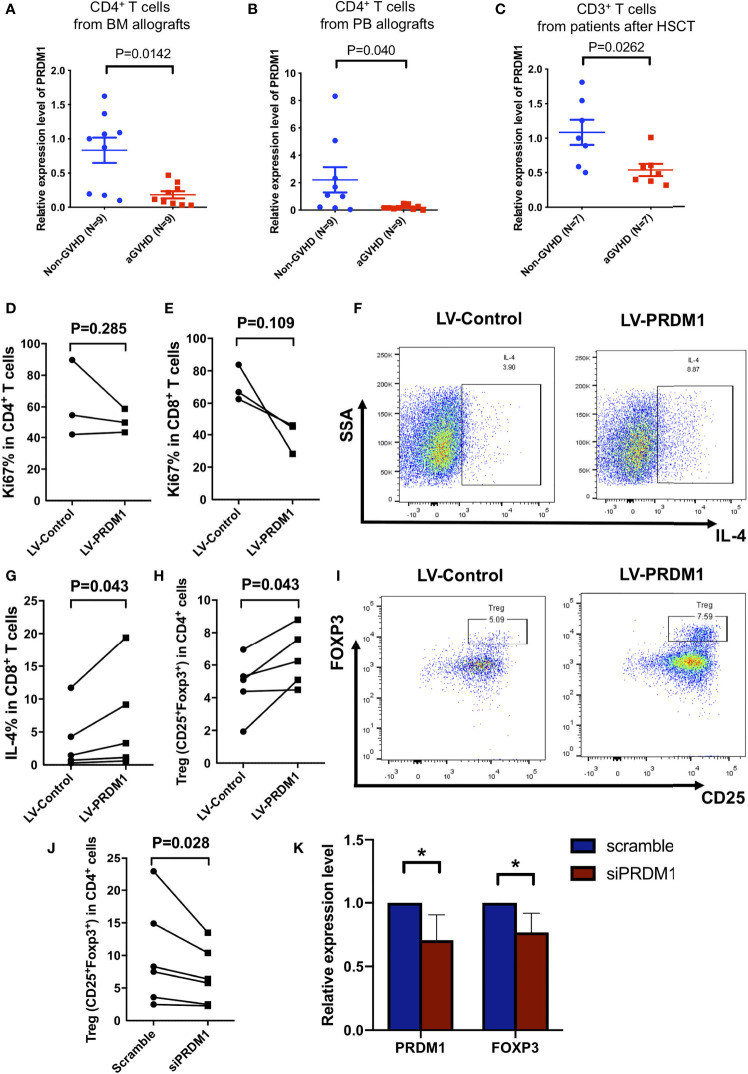
Figure 1.
High expression level of PRDM1 suppressed human primary T cell function. (A, B) Quantitative real-time PCR showed the expression level of PRDM1 in CD4+ T cells from bone marrow allografts (A) and from peripheral allografts (B) and the aGVHD occurrence in related patients, respectively. (C) The expression level of PRDM1 in peripheral CD3+ T cells in patients with aGVHD (n = 7) after allo-HSCT compared with those without aGVHD (n = 7) in the same period. Mann–Whitney U test was used for testing PRDM1 expression. (D, E) Flow cytometry results showed the percentage of Ki67 expression level on PRDM1 overexpressing CD4+ T cells (D) and CD8+ T cells (E) in GFP+ population compared with control T cells (n = 3). (F, G) Representative flow cytometry results and percentages showed the IL-4 secretion level of PRDM1 overexpressing GFP+CD8+ T cells compared with control T cells (n = 5). (H, I) Percentages and representative flow cytometry results showed the Treg cell subset (CD4+CD25+FOXP3+) in PRDM1 overexpressing GFP+CD3+ T cells compared with control T cells (n = 5). (J) Percentage of Treg cell subset in PRDM1 knocked down T cells compared with control T cells (n = 6). (K) Quantitative real-time PCR was used to detect PRDM1 and FOXP3 expression level in PRDM1 knocked down T cells compared with control T cells (n = 6). Wilcoxon rank sum test was performed to assess the significance in D-K. *P < 0.05.