Figure 2.
TIR-APAZ NAD(P)ase activity is controlled by short pAgo
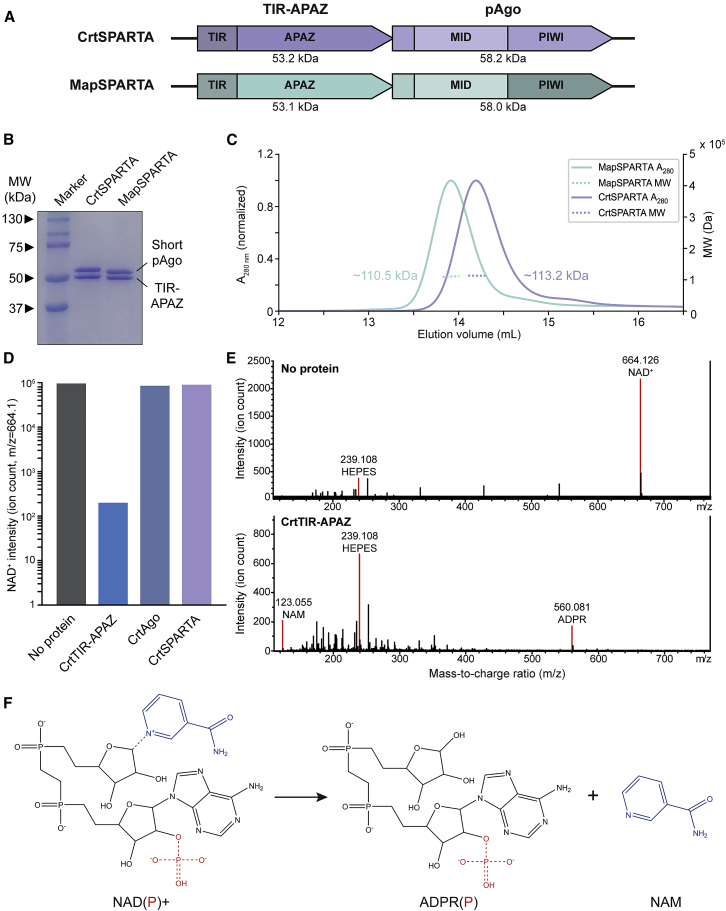
(A) Schematic diagram of CrtSPARTA and MapSPARTA operon structure and domain organization.
(B) TIR-APAZ binds to short pAgo. SDS-PAGE of copurified TIR-APAZ and short pAgo proteins.
(C) TIR-APAZ and short pAgo form SPARTA complexes with a 1:1 stoichiometry. The molecular weight (MW) determined by size exclusion chromatography-multi-angle light scattering corresponds to the theoretical MW of heterodimeric CrtAgo-CrtTIR-APAZ (111.4 kDa) and MapAgo-MapTIR-APAZ (111.1 kDa) complexes.
(D and E) TIR-APAZ is an NADase, and short pAgo inhibits TIR-APAZ activity. LC-MS ion count (D) and spectra (E) for NAD+ after incubation with CrtSPARTA proteins. NAD+ is converted to nicotinamide (NAM) and adenosine diphosphate ribose (ADPR) upon incubation with CrtTIR-APAZ but not when incubated with CrtAgo or CrtSPARTA.
(F) Reaction structural formulas of TIR-APAZ-mediated NAD(P)+ hydrolysis. Blue dotted line: scissile bond.
See also Figure S2.