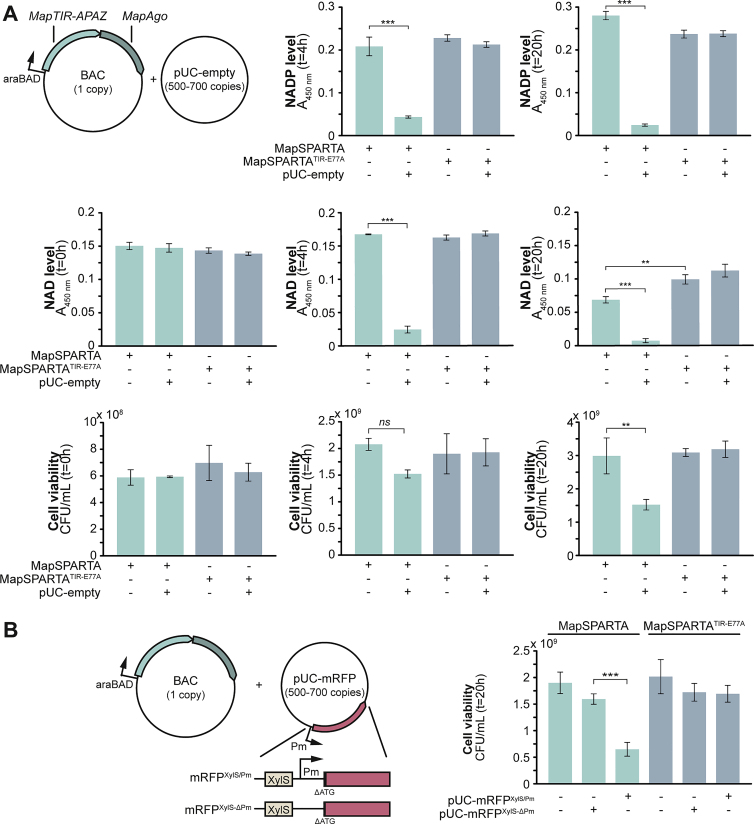
Figure S5.
Plasmid DNA triggers SPARTA-mediated NAD(P) depletion and cell death, related to Figure 5
(A) Plasmid DNA triggers SPARTA-mediated NAD(P) depletion and cell death. NAD and NADP levels and viability were determined in E. coli cultures expressing MapSPARTA or MapSPARTATIR-E77A in the presence or absence of the high copy pUC-empty plasmid. Panels showing NAD levels at t = 4 and cell viability at t = 20 are identical to those in Figure 5A.
(B) Native RNA polymerase-mediated transcription of plasmid-encoded genes enhances SPARTA-mediated cell death. Cell viability was determined in E. coli cultures expressing MapSPARTA or MapSPARTATIR-E77A either in the absence of plasmid DNA or in the presence of a pUC-derivate from which mRFP is transcribed but not translated (pUC-mRFPXylS-Pm) or encoded but not transcribed (pUC-mRFPXylS-ΔPm). The Pm promoter induces transcription by native RNA polymerases. Graphs show the average of three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviations. n.s = not significant; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.