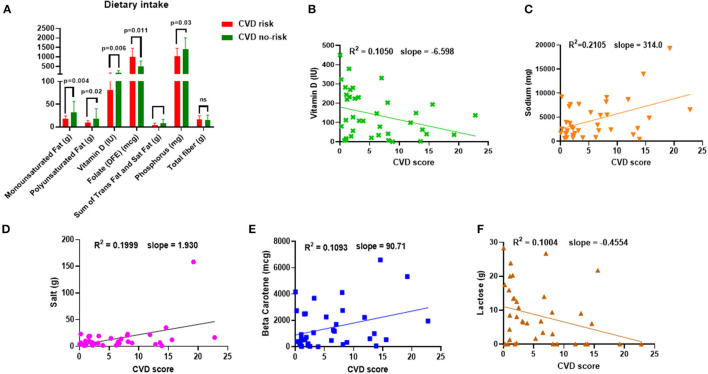
Figure 1.
Dietary intake and correlation to CVD risk. (A) Dietary intake of MUFA, PUFA, vitamin D, folate, the sum of trans-fat and saturated fat, phosphorus, and total fiber in the CVD no-risk and CVD risk groups. (B–F) Correlation analysis of nutrient intake (sodium, salt, beta-carotene, lactose, and vitamin D) and CVD risk in the obese population. CVD no-risk N = 30; CVD risk N = 8. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant using Student's t-test or Mann-Whitney test was performed, wherever applicable.