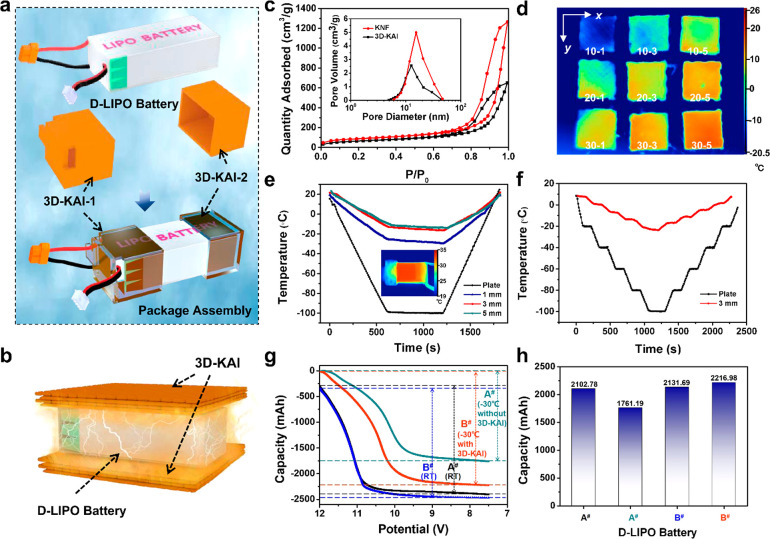
Figure 3.
Thermal insulation performance of the 3D-KAI with spatially stereoscopic structure. (a) Designed models and package assembly of the 3D-KAI-1 and 3D-KAI-2. (b) Schematic illustration of the aerogel layer for thermal insulation performance. (c) Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms of the 3D-KAI and reported KNF aerogel. The inset in part c is the corresponding pore volume. (d) Infrared images of 3D-KAI with different printing densities (10, 20, 30 mg cm–3, the number before hyphen) and thicknesses (1, 3, 5 mm, the number after hyphen). (e,f) Temperature–time curves of the 3D-KAI with different thicknesses (0 (i.e., plate), 1, 3, 5 mm). The inset in part e is the thermal images of the D-LIPO coated with a 3D-KAI. (g) The discharge curves of the D-LIPO with or without the coating of the 3D-KAI. (h) The capacity comparison of the D-LIPO with or without the coating of the 3D-KAI. The A# in black color refers to D-LIPO labeled with A# discharged at room temperature, the B# in blue color refers to D-LIPO labeled with B# discharged at room temperature, the A# in green color refers to D-LIPO labeled with A# discharged at −30 °C, the B# in red color refers to D-LIPO labeled with B# coated with 3D-KAI discharged at −30 °C.