Figure 5.
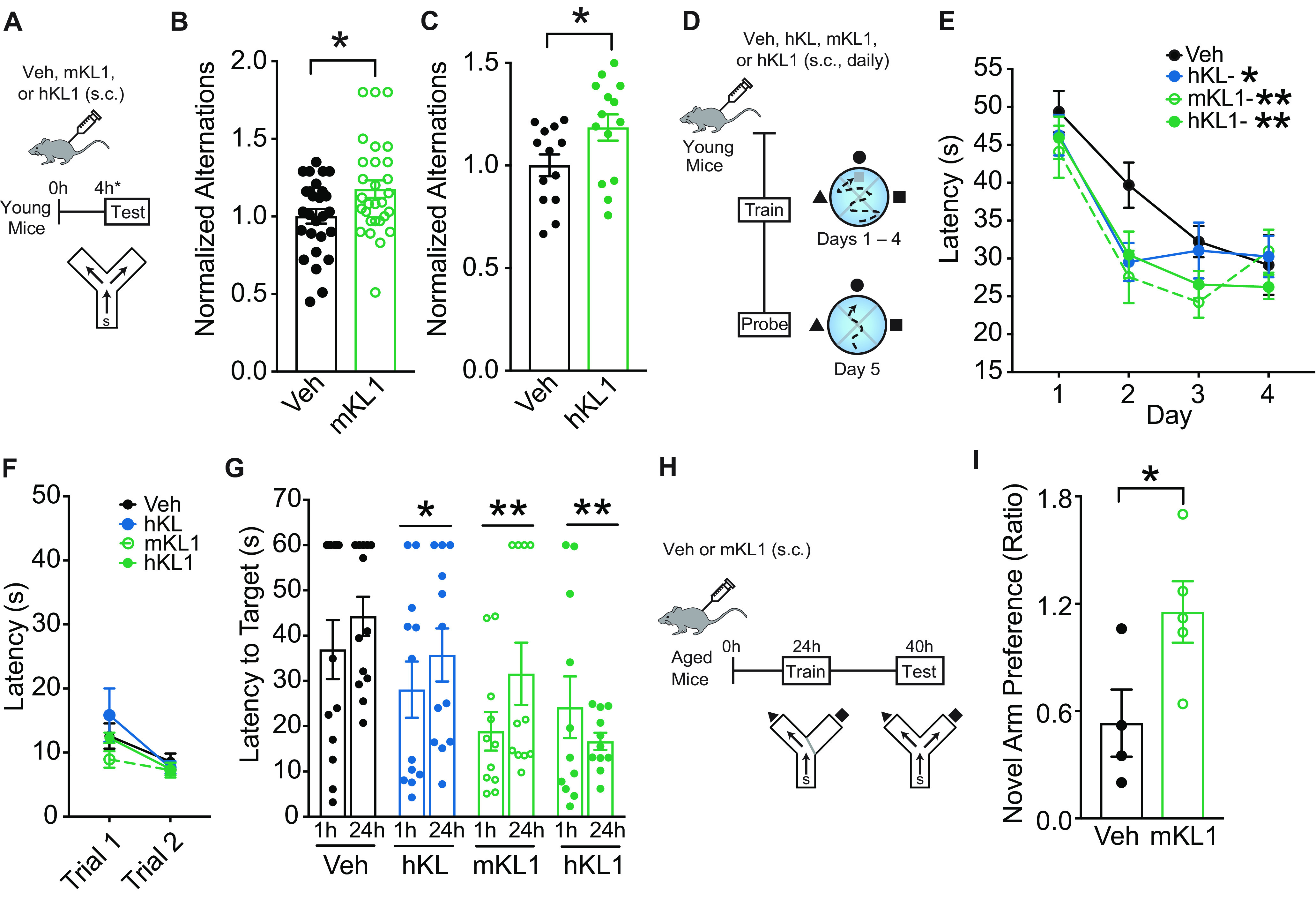
KL1 enhances cognition in young mice and counters cognitive deficits in old mice. A, Experimental paradigm for testing mice (age, 4 months) in the small Y maze following treatment with vehicle (Veh) or KL1 (mouse or human form: 10 μg/kg, s.c.). B, Alternations of mice treated with vehicle or mKL1 (n = 27–29/experimental group). Data expressed relative to control group. *p = 0.0212, df = 54 (two-tailed t test). C, Alternations of mice treated with vehicle or hKL1 (n = 13–14 mice/experimental group). Data are expressed relative to control group. *p = 0.0372, df = 25 (two-tailed t test). D, Experimental paradigm for testing spatial learning and memory of mice in the Morris water maze. Mice were injected daily with vehicle, hKL (10 μg/kg, s.c.), mKL1 (10 μg/kg, s.c.), and hKL1 (10 μg/kg, s.c.). E, Spatial learning curves (platform hidden) in the water maze in mice treated with vehicle, hKL, mKL1, and hKL1 (n = 11–13 mice/experimental group). Data represent the daily average of the latency (in seconds) to find the location of the hidden platform. All KL and KL1 groups enhanced learning compared with vehicle group (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA): Treatment: p = 0.0071, F(3,44) = 4.577; Veh versus hKL (*q = 0.0223); Veh versus mKL1 (**q = 0.0020); Veh versus hKL1 (**q = 0.0034; post hoc corrected q values, Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli test). F, Trials with platform visible, showing no differences in the ability to find a visible target among experimental groups. G, Probe trials conducted 1 and 24 h after hidden training and removal of the escape platform. KL and KL1 (mouse or human) decreased latency to find the target platform, indicating memory enhancement (n = 11–13 mice/experimental group). Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA: Treatment: p = 0.0072, F(3,43) = 4.582; Veh versus hKL (*q = 0.0464); Veh versus mKL1 (**q = 0.0059); Veh versus hKL1 (**q = 0.0012; post hoc corrected q values, Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli test). H, Experimental paradigm for testing working and spatial memory of old mice (age, 22 months) in the two-trial Y maze. Old mice were injected with vehicle or mKL1 (10 μg/kg, s.c.) and then underwent testing and training. I, Spatial and working memory of young and aging mice treated with Veh or mKL1 was assessed by the two-trial Y maze (n = 4–5/experimental group). mKL1 increased the ratio of the percentage of time spent in the novel versus familiar arms during testing at 3 min, indicating improved memory. *p = 0.0450, df = 7 (two-tailed t test). Values represented are data ± SEM. Veh, Vehicle. mKL1, mouse KL1. hKL1, human KL1. hKL, human KL.
