Figure 3.
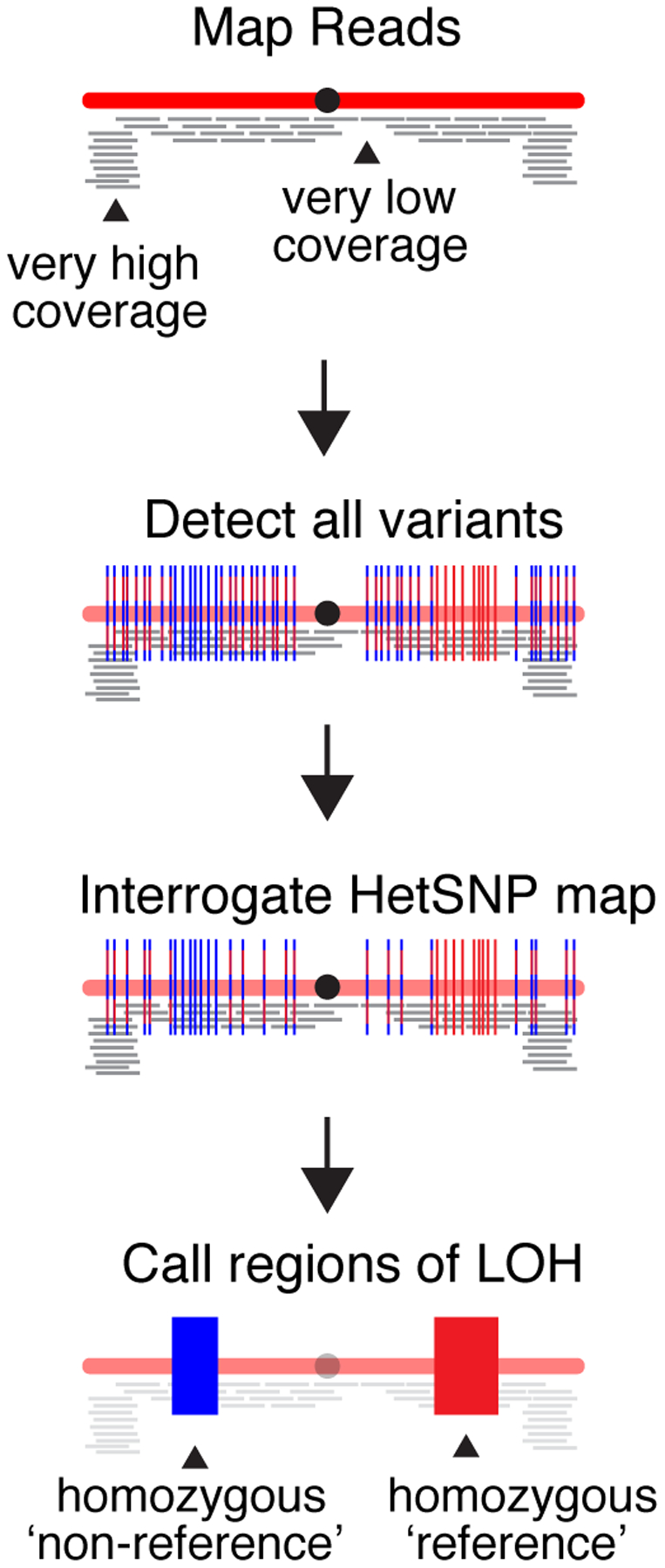
Summary of the approach used to identify tracts of LOH. Sequencing reads are mapped to the S288c reference genome (red) and regions that are excessively over- or under-represented are identified and excluded from further analysis. Next, sequence variants are detected with relaxed stringency. Variants that remained heterozygous are shown as red/blue dashed lines. Variants that have become homozygous are shown as either solid red or solid blue lines. Following low-stringency variant detection, specific allele frequency data are interrogated and retrieved for only HetSNP positions known to exist in the parent diploid. The remaining variants are filtered out and not considered further. Finally, LOH calls are made based on the allele frequencies at the HetSNP positions.
