Figure 4.
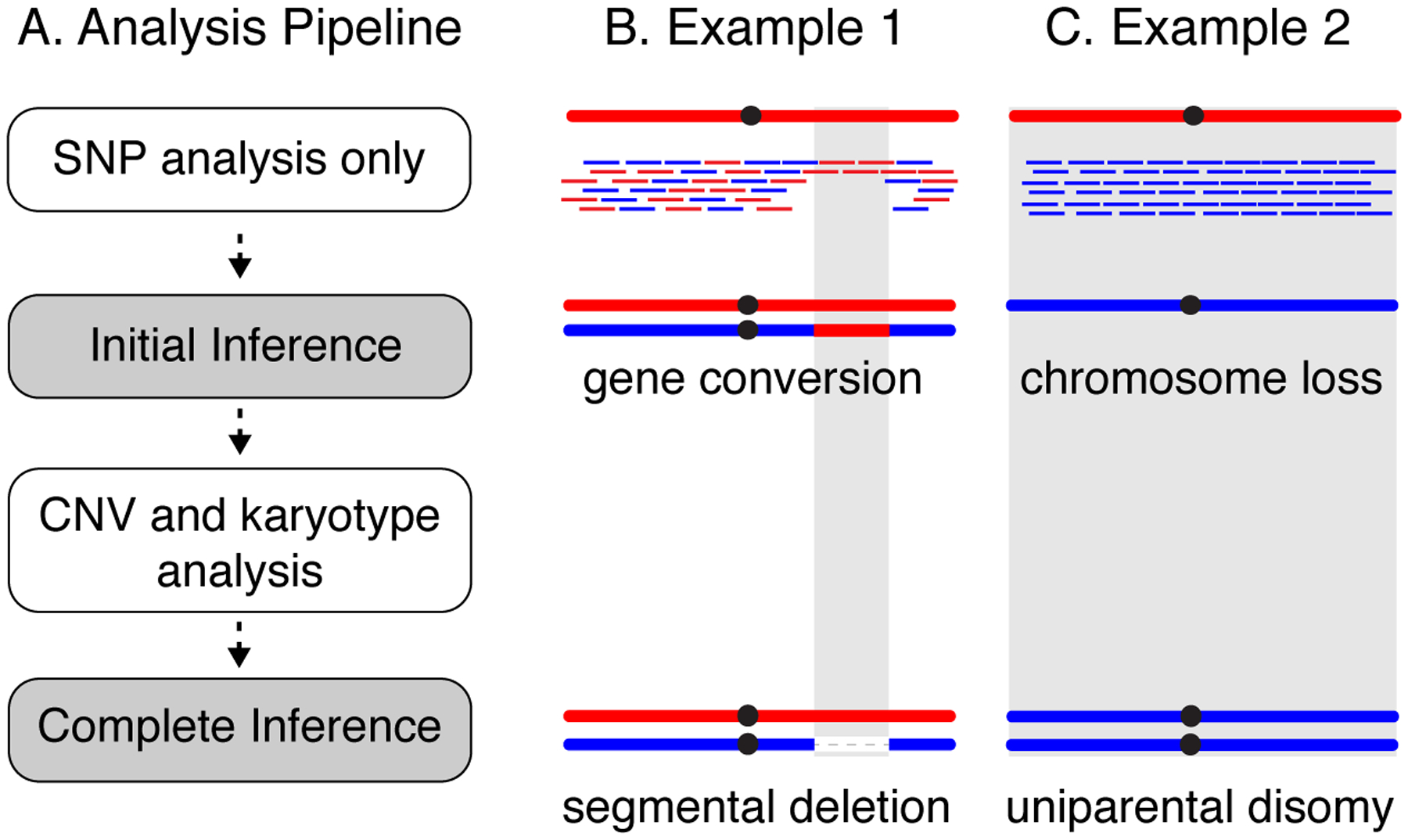
CNV analysis is used in conjunction with HetSNP analysis to refine inferences of genotype and genome structure. A) First, use HetSNP analysis to identify LOH tracts. This alone can lead to an incomplete inference of genotype and genome structure. Next, perform CNV and karyotype analysis. With these additional data, refined inferences of genotype and genome rearrangement mechanisms can be made. B) Example 1, HetSNP genotyping alone would suggest that this clone has become homozygous for a region of red homolog. However, CNV analysis detects a ~50% lower coverage in the region, indicating that that this LOH genotype is in fact caused by a segmental deletion on the blue homolog. C) Example 2, HetSNP genotyping would suggest that this clone has become monosomic due to loss of the red homolog. CNV analysis detects coverage similar to the median for rest of the genome, indicating that the clone is actually disomic for the blue chromosome (uniparental disomy).
