FIGURE 2.
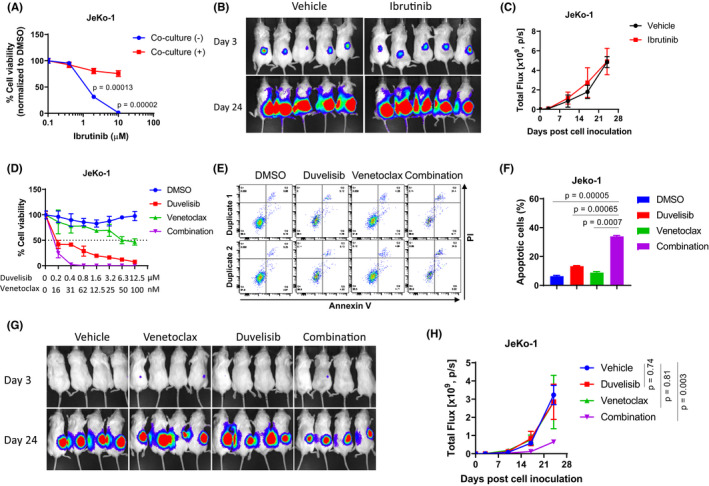
Duvelisib and venetoclax in combination circumvents TME‐mediated ibrutinib‐resistance in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vitro efficacy of ibrutinib in JeKo‐1 cells with or without co‐culture with HS‐5 cells at 72 h post‐treatment. (B, C) NSG mice were injected subcutaneously with 5 × 106 JeKo‐Luc cells per mouse and treated orally once a day with vehicle or ibrutinib (50 mg/kg). Treatment was started on Day 3 following cell inoculation, and tumour burden was measured at Days 3, 17 and 24 post‐treatment by live imaging (B) and by luminescent flux (C). (D) 72‐h dose‐dependent cell viability assay performed on JeKo‐1 cells co‐cultured with HS‐5 cells. (E‐F) 24‐h cell apoptosis assay was conducted in JeKo‐1 cells co‐cultured with HS‐5 cells. The cells were treated with vehicle, 5 μM duvelisib, 100 nM venetoclax or the combination. Cell apoptosis was determined by annexin‐V/PI staining and flow cytometry, and both annexin‐V+/PI− and annexin‐V+/PI+ subpopulations were calculated as apoptotic cells. (E) Representative flow cytometry data are shown for each treatment. (F) Plotted percentile values of apoptotic cells are shown for each treatment. Each cell viability and apoptosis assay were set up in triplicate and repeated at least two independent times. (G, H) 5 × 106 JeKo‐Luc cells were injected into NSG mice subcutaneously and the tumour burden was measured by live imaging. Treatments were started 3 days after cell inoculation. Mice (n = 4) were treated orally, once a day, with vehicle, venetoclax (50 mg/kg), duvelisib (50 mg/kg), alone or in combination. (G) Luminescent images of live mice are shown for Day 3 and Day 24 post‐treatment. (H) Luminescent flux values plotted at days 3, 17 and 24 are shown for each treatment arm
