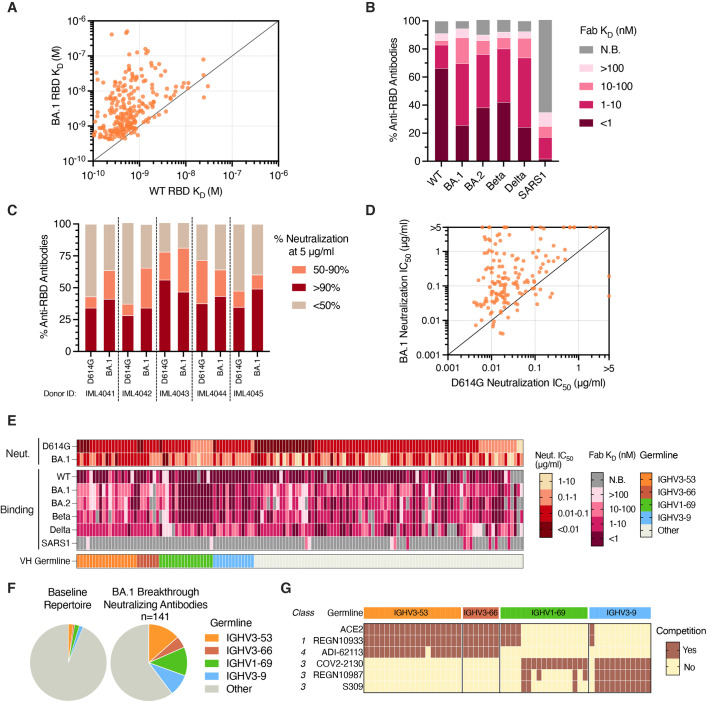
Fig. 4.
Binding and neutralization properties of anti-RBD antibodies isolated following BA.1 breakthrough infection. (A) Fab binding affinities for recombinant WT and BA.1 RBD antigens, as measured by BLI. Fabs with no detectable binding activity or with binding kinetics that could not be fit to a 1:1 binding model were excluded. (B) Proportion of BA.1-reactive antibodies with the indicated binding affinities for SARS-CoV-2 VOC RBDs and SARS-CoV RBD, as measured by BLI. Antibodies with weak binding affinities that could not be fit to a 1:1 binding model are shown as >100 nM, and antibodies with no detectable Fab binding, including those that bind only avidly, are indicated as non-binding (N.B.). (C) Proportion of antibodies from each donor with the indicated levels of neutralizing activity against MLV-SARS-CoV-2 D614G and BA.1 at a concentration of 5 μg/ml. (D) MLV-SARS-CoV-2 D614G and BA.1 neutralization IC50s for antibodies that displayed >90% neutralization against D614G and/or BA.1 at a concentration of 5 μg/ml. (E) Heatmap showing neutralization potency and binding breadth of BA.1 neutralizing antibodies. The bottom bar shows convergent IGHV germline gene families. Antibodies with weak binding affinities that could not be fit to a 1:1 binding model are shown as >100 nM, and antibodies with no detectable Fab binding are indicated as non-binding (N.B.). (F) Pie charts showing convergent germline gene usage among (right) BA.1-neutralizing antibodies compared to the (left) baseline human antibody repertoires ( 22 ). (G) Competitive binding profiles of BA.1 neutralizing antibodies utilizing convergent IGHV germline genes, as determined by BLI sandwich competition assay using ACE2 and the indicated comparator antibodies. Fab, antigen binding fragment; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; IGHV, immunoglobulin gene heavy variable; KD, equilibrium dissociation constant; N.B., non-binding; WT, wild type.