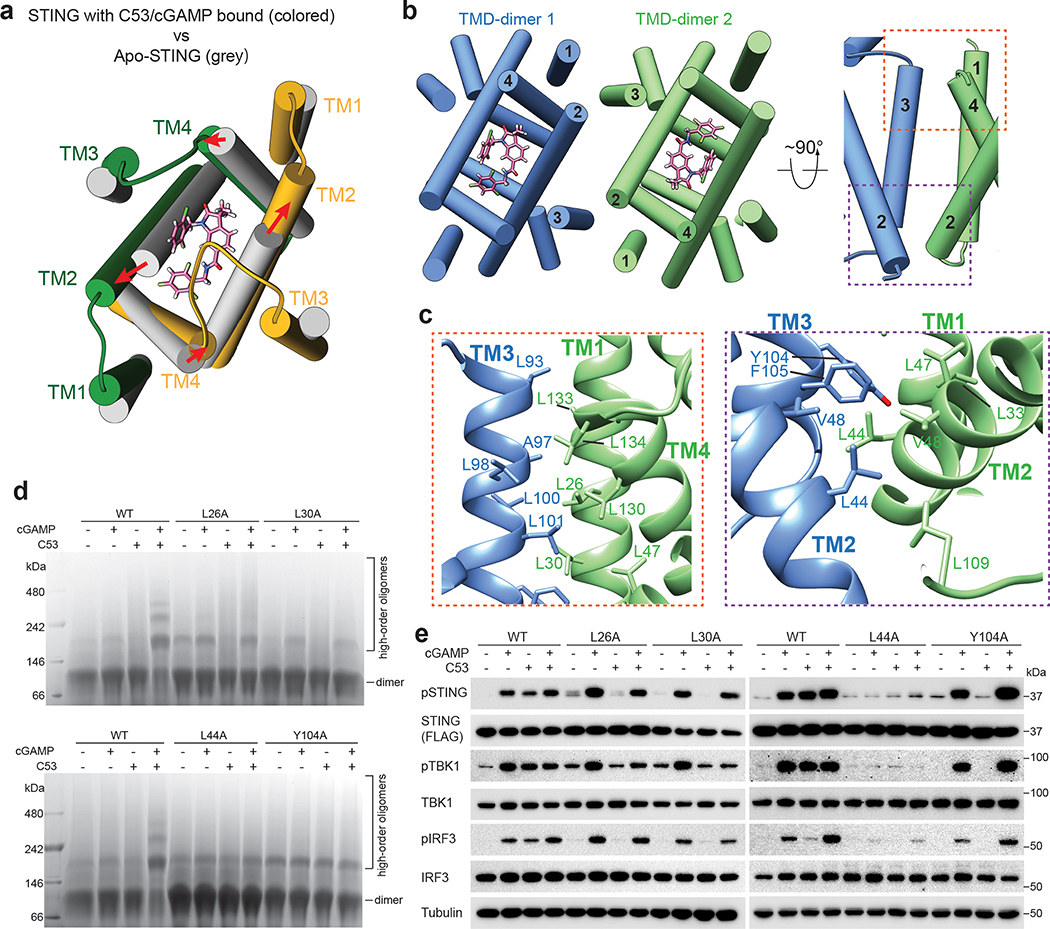
Fig. 4. TMD-mediated interactions contribute to STING oligomerization.
a, C53 induces dilation of the TMD binding pocket in the STING dimer. A comparison with apo-STING shows that the TM helices in the C53-bound structure shift away from each other to enlarge the binding pocket. The structure is viewed from the ER/Golgi luminal side. b, Two orthogonal views of the TMD-TMD interface between the two STING dimers. TM3 from one dimer joins one set of TM1, TM2 and TM4 from the other dimer to form a four-helix bundle. c, Detailed views of the TMD-TMD interface. d, Effects of mutations in the TMD-TMD interface on STING oligomerization induced by cGAMP and C53. Native gel results shown are representatives of three biological repeats. e, Effects of mutations in the TMD-TMD interface on phosphorylation of STING, TBK1 and IRF3 induced by cGAMP and C53 in cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with human STING wild type or the mutants. Cells were stimulated with cGAMP, C53 or both and lysates were subjected to western blot analyses. The results shown are representatives of three biological repeats. For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1.