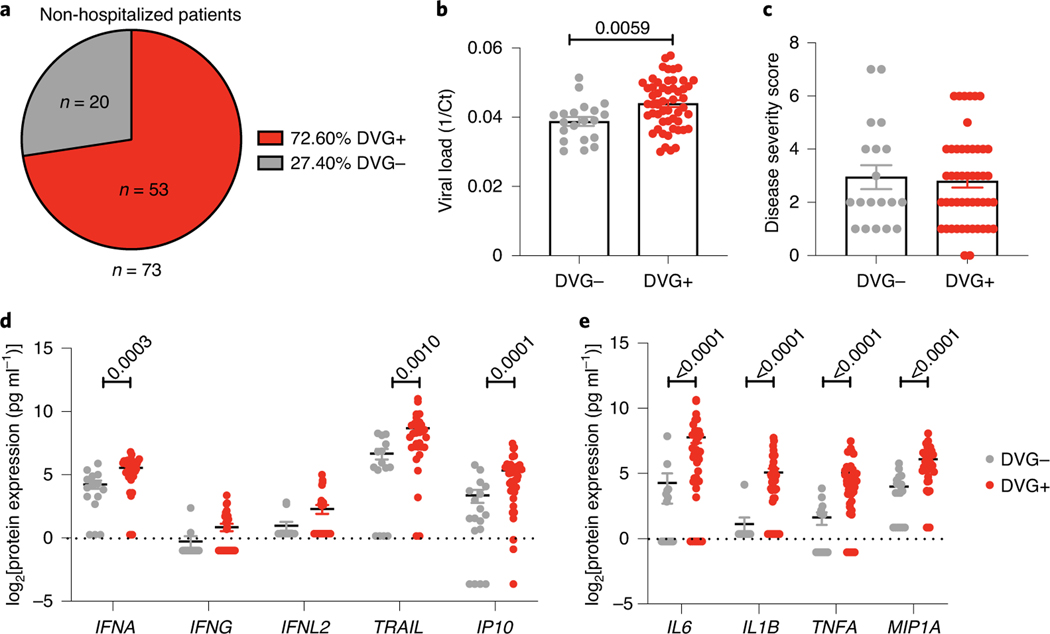
Fig. 3 |. cbDVg+ non-hospitalized paediatric patients do not have worse respiratory disease than cbDVg− patients.
a, Pie chart showing the percentage and actual number of cbDVG+ and cbDVG− patients among non-hospitalized paediatric patients detected by PCR. b,c, In the 73 non-hospitalized infants, viral load (b) and disease severity score (c) were compared in patients with (n = 53, red) and without cbDVGs (n = 20, grey). Viral load was determined by Ct values from RT–qPCR and is plotted as 1/Ct. d,e, Scattered dot plots showing (d) expression of IFNA and representative ISGs and (e) representative pro-inflammatory cytokines from cbDVG− (n = 15–18; grey) and cbDVG+ (n = 30–41; red) non-hospitalized paediatric patients. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. Significant P values for two-tailed Mann–Whitney test are indicated.