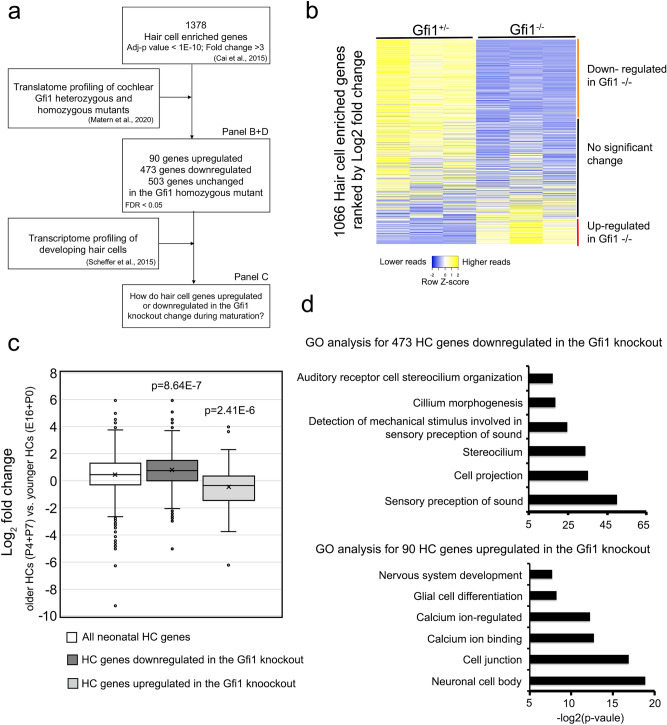
Figure 1.
GFI1 differentially regulates expression of hair cell genes during inner ear development. (a) Overview of the analysis workflow: We used our previously published RNA-seq data from neonatal hair cells38 to identify a list of 1378 genes enriched in hair cells. We then cross-referenced this list with RNA-seq translatome data from Gfi1 mutant or heterozygote hair cells30 to identify genes that were up-or-down-regulated in Gfi1 null mice. We then examined how expression of these GFI1-regulated genes varied in hair cells with developmental time, but using data from E16, P1, P4 and P7 purified hair cells40. (b) Heat map for the expression of hair cell-enriched genes in Gfi1 heterozygous and null mice showing. The orange-labeled cluster represents genes significantly downregulated in Gfi1 homozygous mutant hair cells, the red-labeled cluster represents genes that are significantly upregulated in the Gfi1 mutant, and the black-labeled cluster shows genes that are not significantly changed in mutant hair cells. (c) Box plot showing that the 473 hair cell genes that are down-regulated in the Gfi1 knockout tend to be expressed at higher levels in more mature (P4 and P7) hair cells, while the 90 hair cell genes that are up-regulated in the Gfi1 knockout tend to be expressed at a lower level in more mature hair cells. Statistical significance was assessed by a Student t-test, comparing the Log2 fold change (FC) values of each gene group to the log2 FC values of all neonatal hair cell genes. (d) Gene ontology analysis of hair cell-enriched genes that are either down-regulated (473 genes) or up-regulated (90 genes) in the Gfi1 knockout.