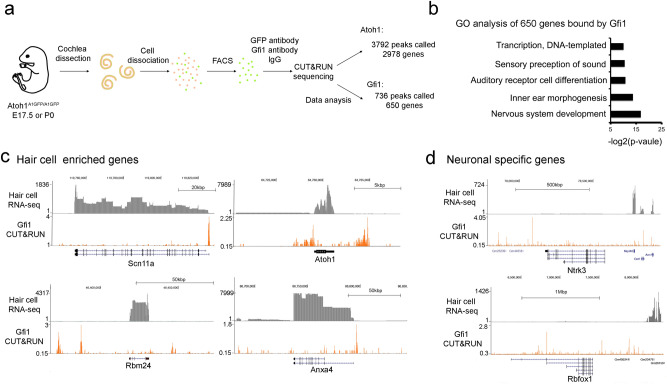
Figure 2.
GFI1 directly binds to many genomic loci that it positively or negatively regulates. (a) Diagram of the CUT&RUN sequencing experiment. Cochleas from Atoh1A1GFP mice in which the hair cell transcription factor ATOH1 is fused to GFP were dissected, dissociated into single cells and FACS-sorted. Purified hair cells were processed for CUT&RUN sequencing with antibodies to either GFP (to identify ATOH1 targets), GFI1, or an IgG control. (b) Gene ontology analysis of the 650 GFI1 binding genes. (c) Genomic browser track of CUT&RUN sequencing showing examples of GFI1 binding to loci near four hair cell genes: Scn11a, Atoh1, Rbm24, and Anxa4. With the exception of Atoh1, they are all downregulated in the Gfi1 knockout cochlea30. (d) Genomic browser track of CUT&RUN sequencing showing examples of GFI1 binding loci near known neuronal-specific genes, Ntrk3 and Rbfox that are upregulated in the Gfi1 knockout cochlea30. As shown in the RNA-seq traces, these two genes are normally not expressed in the neonatal hair cells, so the trace scale is expanded in both cases to show RNA-seq traces from nearby genes as a positive control.