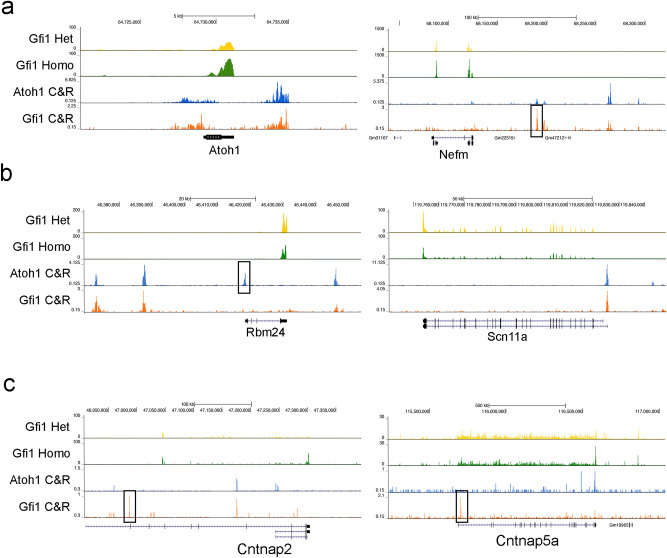
Figure 4.
Examples of hair cell and non-hair cell enriched genes that are bound and regulated by GFI1 and ATOH1. (a) Genomic browser tracks of RNA-seq and CUT&RUN sequencing of two hair cell genes containing both ATOH1 and GFI1 binding sites that are up-regulated in the Gfi1 knockout: Atoh1 (Log2 fold change in homozygous (homo) vs. heterozygous (het) Gfi1 mutants (LFC) = 0.42; False discovery rate (FDR) = 0.0492) and Nefm (LFC = 0.84; FDR = 0.000127). Box shows a peak that is uniquely bound by GFI1. (b) Genomic browser tracks of RNA-seq and CUT&RUN sequencing of two hair cell genes containing both ATOH1 and GFI1 binding sites that are down-regulated in the Gfi1 knockout: Rbm24 (LFC = − 0.85; FDR = 5.25E−07) and Scn11a (LFC = − 0.5; FDR = 0.00245). Box shows a peak that is uniquely bound by ATOH1. (c) Genomic browser tracks of RNA-seq and CUT&RUN sequencing of neuronal (non-hair cell) genes containing both ATOH1 and GFI1 binding sites that are upregulated in the Gfi1 knockout: Cntnap2 (LFC = 2.59; FDR = 3.79E−32) and Cntnap5a (LFC = 0.79; FDR = 6.23E−05). Boxes show peaks that are uniquely bound by Gfi1.