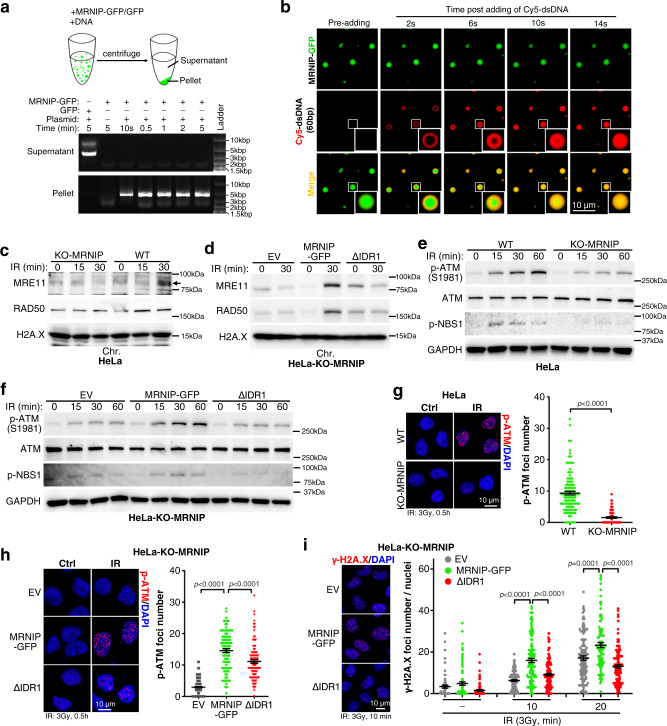
Fig. 5. MRNIP condensates accelerate the MRN complex loading and DNA damage response.
a, b MRNIP condensates incorporated DNA from solutions within 10 s. Ten micromolar MRNIP was incubated with 15 ng/µL plasmid DNA or 0.5 µM Cy5-dsDNA in buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4. c MRNIP depletion reduced radiation-induced MRN complex binding to chromatin. d The impact of wild-type or IDR1-deleted MRNIP on the radiation-induced binding of the MRN complex to DNA. For (c, d), chromatin was fractionated at the indicated time after irradiation (10 Gy). EV, empty vector; ΔIDR1, MRNIP-ΔIDR1-GFP. e, f The impact of MRNIP condensates on radiation-induced ATM and NBS1 phosphorylation. IR: 3 Gy. g, h IF assays were performed to analyse the impact of MRNIP on radiation-induced ATM phosphorylation. HeLa cells were irradiated with 3 Gy. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. g n = 116 (WT), n = 77 (KO-MRNIP). h n = 107 (EV), n = 93 (MRNIP-GFP), n = 103 (ΔIDR1). i IF assays were performed to analyze the impact of MRNIP on radiation-induced γ-H2A.X phosphorylation. HeLa cells were exposed to 3 Gy X-ray. Data are presented as means ± SEM. IR-: n = 69 (EV), n = 87 (MRNIP-GFP), n = 87 (ΔIDR1); IR 10 min: n = 124 (EV), n = 122 (MRNIP-GFP), n = 119 (ΔIDR1); IR 20 min: n = 111 (EV), n = 96 (MRNIP-GFP), n = 112 (ΔIDR1). Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. For (c–i), HeLa-KO-MRNIP cells stably expressing sgRNA-resistant MRNIP-GFP, MRNIP-ΔIDR1-GFP (ΔIDR1) and empty vector (EV) were used.