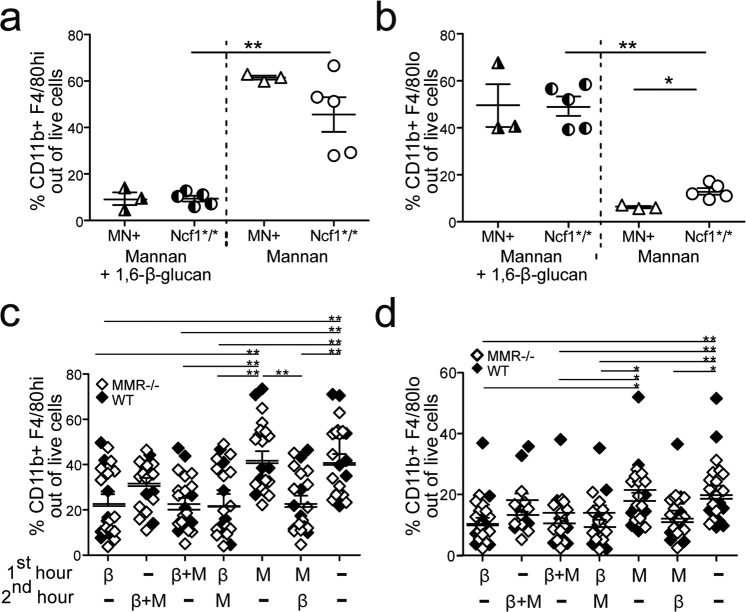
Fig. 5. 1,6-β-glucan decreases the number of resident peritoneal macrophages.
Resident (a) and infiltrating (b) macrophages were measured among live peritoneal cells collected day 8 after induction of MIP with or without co-administration of 1,6-β-glucan (2 mg) in Ncf1*/* and MN + mice. For analysis of cell phenotypes after in vitro stimulation (c, d), naive peritoneal cells were collected from MMR−/− and WT mice and challenged in vitro for a total of 2 h, using two different stimulation points (1 h in between), with mannan (M) and/or 1,6-β-glucan (β) without washes between the treatments. Resident macrophages were defined as CD11b + F4/80hi (in a and c) and infiltrating macrophages as CD11b + F4/80lo (in b and d), as determined by flow cytometry. Data in (c, d) are a combination of two experiments with total n = 21. Statistical analyses were performed with Mann–Whitney test (a, b) and one-way ANOVA using Bonferroni post test (c, d). *P < 0.05; and **P < 0.01. Results are presented as mean with SEM.