Fig. 5. A model for the behaviour of FtsA during divisome activation.
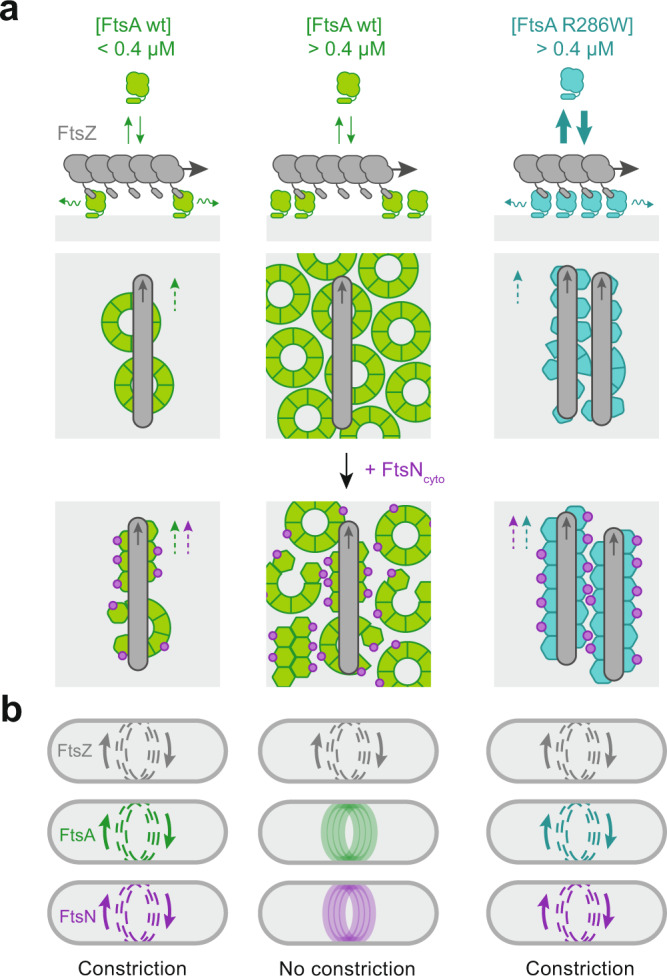
The spatiotemporal distribution of FtsA is the result of its dynamic interaction with treadmilling FtsZ filaments and the lipid membrane. Grey arrows indicate FtsZ treadmilling direction, green and cyan arrows represent cycling exchange of FtsA by reversible membrane binding, wavy arrows represent diffusion on the membrane surface, dashed arrows indicate co-treadmilling of FtsA and FtsN with FtsZ. a Left: At low FtsA WT concentrations, i.e. at a protein ratio found in vivo ([FtsA WT] = 0.2 µM, [FtsZ] = 1.25 µM), diffusion of membrane-bound FtsA is fast enough to allow for co-treadmilling despite slow-cycling rates. The presence of FtsA WT minirings limits the packing density and therefore its amount recruited to FtsZ filaments. Furthermore, FtsA minirings allow for a continuous realignment of treadmilling filaments. Binding of FtsNcyto leads to the formation of FtsA-FtsN copolymers that follow treadmilling FtsZ filaments and limits their reorganization. Middle: At higher concentrations, FtsA WT forms a continuous array of minirings, stabilized by lateral interactions. Due to the absence of diffusion, FtsA cannot follow FtsZ treadmilling dynamics. Right: Even at high FtsA R286W concentrations, its fast exchange allows co-treadmilling with FtsZ filament. Loss of longitudinal interactions in FtsA R286W disrupts minirings and allows for a higher packing density, which limits the realignment of FtsZ filaments. Binding of FtsN further enhances lateral interactions to promote the formation of FtsA double filaments that further limits realignment of FtsZ filaments. b In vivo, low concentrations of FtsA WT allow for continuous co-treadmilling of FtsZ, FtsA and downstream proteins around the cell diameter, where they distribute cell wall synthesis allowing for cell constriction. When overexpressed, FtsA WT as well as its binding partner FtsN stop following FtsZ treadmilling, cell wall synthesis is not distributed and the cell fails to divide. In the case of FtsA R286W, its fast membrane cycling rate and faster diffusion allows for a dynamic distribution of proteins, constriction and cell division, even when overexpressed.
